VA Construction Loans: 7 Ways to Build Your Dream Home Using Military Benefits

Build Custom Homes With Competitive VA Financing
Military families seeking to build custom homes face unique financing challenges that traditional construction loans don’t address effectively. Frequent relocations, deployment schedules, and varied income structures complicate standard construction financing approaches. VA construction loans provide a specialized solution—combining land acquisition and construction financing with permanent VA loan benefits in a single-close transaction. This comprehensive guide reveals how eligible veterans and service members can leverage VA construction financing to build from the ground up, navigate the approval process, and maximize the advantages earned through military service while creating homes tailored to their specific needs.
Key details you’ll discover:
- How VA construction-to-permanent financing works as a single-close loan eliminating the need for separate construction and permanent financing (VA Construction Loan Overview)
- Builder qualification requirements ensuring contractors meet VA approval standards for licensing, insurance, and financial stability (VA Builder Requirements)
- Construction timeline expectations typically allowing 12 months for project completion with possible extensions for justified delays
- Draw schedule processes releasing funds at predetermined construction milestones after inspector verification
- Property specification standards mandating primary residence use and compliance with VA minimum property requirements (VA Minimum Property Requirements)
- Funding fee structures for construction loans that differ from standard VA purchase financing (VA Funding Fee Chart)
- Certificate of Eligibility requirements proving military service qualifications for VA loan benefits
- Budget considerations including land costs, construction expenses, contingency reserves, and permanent financing conversion
Ready to explore your options? Schedule a call with a loan advisor.
What Is a VA Construction Loan?
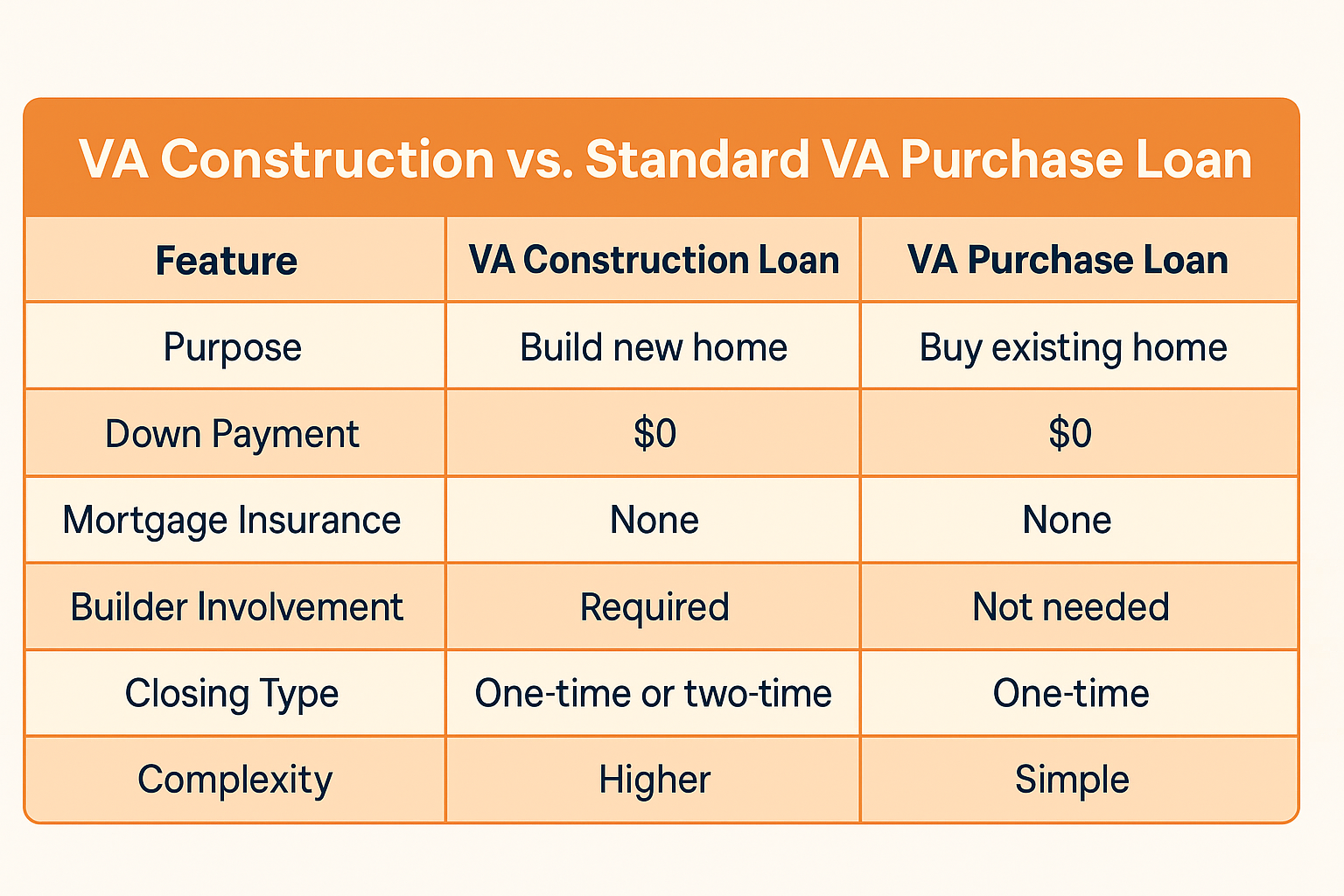
A VA construction loan combines construction financing with permanent mortgage financing in a single-close transaction specifically designed for eligible military families. Unlike traditional construction projects requiring separate construction loans followed by permanent financing, VA construction-to-permanent loans lock in your permanent loan terms at the initial closing, eliminating duplicate closing costs, repeated qualification processes, and interest rate uncertainty during the construction phase.
The VA guarantees these loans through approved lenders, enabling qualified veterans and service members to finance both land purchase and construction costs with the same competitive terms and flexible initial investment options available through standard VA purchase loans. This financing structure serves military families who want to build custom homes but lack substantial cash reserves for traditional construction financing.
How does VA construction financing differ from conventional construction loans?
VA construction loans provide several distinct advantages for eligible military families:
- Single closing process – Lock in permanent loan terms before construction begins, avoiding refinancing uncertainty after project completion
- Competitive VA terms – Access the same favorable structures and flexible initial investment options as standard VA purchase financing
- No private mortgage insurance – Eliminate ongoing insurance premiums required with conventional construction financing
- Flexible funding structures – Finance eligible land costs, construction expenses, and permanent mortgage in one transaction
- Streamlined transitions – Convert automatically from construction phase to permanent financing without additional qualification or closing procedures
- Builder flexibility – Work with any licensed contractor meeting VA approval standards, not just lender-preferred builders
This streamlined approach reduces complexity, eliminates redundant costs, and provides certainty throughout the construction process while leveraging the full range of VA loan benefits.
See how other military families have successfully used VA construction financing:
- View VA construction loan case studies
- View standard VA purchase case studies
- View VA refinance case studies
Who Qualifies for VA Construction Loans?
VA construction loan eligibility centers on military service requirements, creditworthiness, income sufficiency, and builder qualifications. Understanding these requirements helps determine whether this financing option fits your circumstances.
Military Service Requirements
What service qualifications make borrowers eligible for VA construction financing?
VA construction loans follow the same eligibility standards as all VA loan programs:
Active duty service members who have served:
- 90 continuous days during wartime periods
- 181 days during peacetime
- Any duration if discharged due to service-connected disability
Veterans who completed:
- 90 days of active service during wartime with honorable discharge
- 181 days during peacetime with honorable discharge
- 6 years in National Guard or Reserves with honorable discharge
- Any service period if discharged due to service-connected disability
National Guard and Reserve members who have:
- Completed 6 years of service in Selected Reserve or National Guard
- Been discharged honorably or continue serving
- Completed required drills and annual training periods
Surviving spouses who:
- Lost a spouse in service or from service-connected disabilities
- Have not remarried (or remarried after age 57)
- Receive Dependency and Indemnity Compensation
Specific service period requirements vary based on when you served. Review VA eligibility requirements for detailed timelines for different service eras.
Certificate of Eligibility Process
How do you obtain a Certificate of Eligibility for VA construction loans?
Before applying for VA construction financing, obtain your Certificate of Eligibility (COE) documenting your qualification:
- Online application via the VA’s eBenefits portal using your DS Logon credentials
- Through your lender who can request your COE electronically during the application process
- Mail application by submitting VA Form 26-1880 with supporting military documentation
- In-person request at local VA regional offices with appropriate service records
Required documentation varies by service category:
- Veterans: DD Form 214 (Certificate of Release or Discharge from Active Duty)
- Active duty: Statement of Service signed by commander, adjutant, or personnel officer
- Reservists/Guard: DD Form 214 plus points statement showing qualifying service
- Surviving spouses: Marriage certificate, veteran’s DD Form 214, and VA death letter
Most borrowers obtain COEs within minutes through online applications or lender requests. Paper applications typically process within 5-10 business days.
Credit and Financial Requirements
What financial qualifications must VA construction loan applicants meet?
Beyond military eligibility, VA construction loans require:
Credit history demonstrating:
- Responsible payment patterns on past and current obligations
- Resolution of any credit issues with satisfactory explanations
- Reasonable recent credit activity without excessive new accounts
- Overall creditworthiness supporting long-term mortgage commitments
Stable employment showing:
- At least two years in the same field or profession
- Consistent income patterns supporting mortgage obligations
- Reasonable expectation of continued employment
Sufficient income to cover:
- Proposed housing expenses including principal, interest, taxes, and insurance
- Existing debt obligations such as car loans, student loans, and credit cards
- Living expenses appropriate for your family size and geographic location
Residual income meeting VA’s unique requirements that calculate remaining funds after subtracting all monthly obligations, varying by:
- Family size (more members require higher residual income)
- Geographic region (higher cost areas have elevated thresholds)
- Loan amount (larger mortgages need greater residual capacity)
Adequate reserves to cover:
- Closing costs and pre-paid expenses
- Any required reserve requirements beyond closing
- Construction contingency for unexpected project costs
These standards ensure borrowers can successfully manage both construction oversight and long-term mortgage obligations after project completion.
Calculate your personalized construction scenario:
Builder and Contractor Requirements
What qualifications must builders meet for VA construction projects?
VA construction loans require builders and contractors to meet specific qualification standards ensuring project quality and completion. These requirements protect both veterans and the VA by preventing financing with unreliable contractors.
Essential Builder Qualifications
Valid licensing appropriate for:
- The construction type and scope of work
- Local jurisdiction where construction will occur
- All specialized trade work included in the project
- Current status without disciplinary actions or suspensions
Active insurance coverage including:
- General liability insurance protecting against property damage and injury claims
- Workers compensation coverage for all construction employees
- Builder’s risk insurance during the construction phase
- Adequate coverage limits appropriate for project size and complexity
Financial stability demonstrated through:
- Business history showing successful project completions
- Acceptable credit standing without recent bankruptcies or judgments
- Adequate working capital to manage construction cash flow
- Banking relationships supporting construction operations
Construction experience with:
- Documented track record of successful project completions
- References from previous clients, suppliers, and lenders
- Portfolio of comparable projects demonstrating relevant expertise
- Local market knowledge and supplier relationships
Bonding capacity when required by:
- Local regulations mandating performance bonds
- Lender policies requiring completion guarantees
- Project size exceeding certain thresholds
- Risk factors warranting additional security
Vetting Your Builder
How should you evaluate potential contractors for VA construction projects?
Before selecting a builder, verify:
Licensing and credentials:
- Check state licensing board websites for current status
- Verify no disciplinary actions or complaint history
- Confirm licensing covers your project scope
- Request copies of all relevant licenses and certifications
Insurance verification:
- Obtain certificates of insurance directly from insurance companies
- Verify coverage remains current throughout construction timeline
- Confirm coverage limits adequate for your project value
- Check workers compensation coverage for all employees
References and past work:
- Contact at least 3-5 previous clients about their experiences
- Visit completed projects similar to your proposed construction
- Check with local suppliers about payment history and reputation
- Review online ratings and Better Business Bureau records
Financial standing:
- Request financial statements or bank references
- Verify no recent bankruptcies or significant judgments
- Confirm adequate working capital for your project
- Check payment history with subcontractors and suppliers
Lenders review builder qualifications during the approval process, but conducting your own due diligence protects against selecting problematic contractors who might delay your project or create quality issues.
The VA Construction Loan Process
What steps are involved in obtaining VA construction financing?
The VA construction loan process follows a sequential path from initial planning through project completion and conversion to permanent financing.
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
Before applying for VA construction financing:
- Select and purchase land (or verify owned land eligibility) in a location where you’ll establish primary residence
- Choose a qualified builder who holds appropriate licensing and meets VA approval standards
- Develop construction plans with architectural drawings, specifications, and material selections
- Obtain detailed cost estimates covering land acquisition, construction expenses, and contingency reserves
- Verify military eligibility and obtain Certificate of Eligibility if not already done
- Review credit standing and address any issues that might delay approval
- Confirm adequate reserves for closing costs and required reserve amounts
This preparation phase typically requires 60-90 days depending on land acquisition timing, plan complexity, and builder availability.
Phase 2: Application and Approval
What documentation is required for VA construction loan applications?
The formal application process includes:
- Submit loan application with a VA-approved lender experienced in construction financing
- Provide military documentation including Certificate of Eligibility and service records
- Supply income verification through tax returns, pay stubs, bank statements, and employer documentation
- Submit construction details including:
- Complete architectural plans and specifications
- Itemized cost breakdown from builder
- Construction timeline and milestone schedule
- Builder’s license, insurance, and financial information
- Land documentation showing ownership or purchase agreement
- Order property appraisal based on projected completed value using construction plans and comparable sales
- Undergo underwriting review where lenders verify all eligibility requirements and construction feasibility
- Receive conditional approval subject to any outstanding documentation or plan modifications
- Address conditions by supplying requested information or making specified adjustments
- Obtain final approval clearing the path for closing and construction commencement
This application and approval phase typically requires 45-90 days depending on documentation completeness, appraisal complexity, and underwriting workload.
Phase 3: Construction Phase
How does funding work during the construction period?
After loan approval and initial closing, construction proceeds through a structured draw process:
Initial disbursement covering:
- Land purchase if not already owned
- Site preparation and foundation work
- Initial construction expenses bringing project to first milestone
Progress draws releasing funds at predetermined milestones:
- Foundation completion
- Framing and roof installation
- Rough mechanical systems (plumbing, electrical, HVAC)
- Drywall completion
- Interior finishes and fixtures
- Final completion and occupancy readiness
Inspector verification before each draw:
- Lender-appointed inspector confirms completed work meets plans and specifications
- Quality review ensures construction meets VA standards
- Verification that work matches draw request amounts
- Documentation of completion before releasing funds
Builder coordination throughout construction:
- Regular communication on project progress
- Addressing any modifications or issues promptly
- Managing timeline to meet approved completion schedule
- Submitting draw requests with supporting invoices and lien waivers
Most VA construction loans allow 12 months for project completion, with possible extensions for justified delays caused by weather, material shortages, permitting issues, or other circumstances beyond contractor control.
Phase 4: Conversion to Permanent Financing
What happens when construction completes?
Upon construction completion, the loan converts automatically to permanent VA financing:
- Final inspection confirms the property meets all plans, specifications, and VA minimum property requirements
- Certificate of occupancy issued by local authorities permits legal residence
- Final disbursement releases any remaining construction funds to the builder
- Conversion to permanent loan activates standard mortgage payment schedule
- Payment commencement typically begins 30-60 days after conversion
- Occupancy requirement mandates moving into the property within 60 days of completion
This seamless transition eliminates the need for refinancing, additional qualification, or exposure to interest rate changes that could occur during construction. The terms locked at initial closing remain in effect for the permanent financing phase.
Ready to discuss your construction scenario? Submit a purchase inquiry to explore your options.
Common Questions About VA Construction Loans
Can You Use a VA Construction Loan for Land Purchase?
Yes. VA construction loans can finance both land acquisition and construction costs in a single transaction. This approach works whether you already own eligible land or need to purchase property as part of the construction project.
When purchasing land as part of the loan:
- The land must be in a location where you’ll establish primary residence
- Combined land and construction costs determine your total loan amount
- Land purchase typically closes simultaneously with construction loan funding
- Title work covers both land acquisition and construction financing
When you already own land:
- The land must meet VA requirements for buildable residential property
- Your existing equity doesn’t necessarily reduce financing needs since VA loans offer flexible initial investment options
- Recent land purchases may require documentation showing acquisition price and payment source
- Land must be free of liens or encumbrances that would impair construction
Whether purchasing new land or building on property you own, the VA construction loan covers all eligible costs in one financing package.
What Types of Homes Can You Build With VA Construction Loans?
What property types qualify for VA construction financing?
VA construction loans apply to specific property types:
Single-family detached homes built as primary residences meeting VA property standards
Modular homes constructed to local building codes (not just HUD standards) and permanently affixed to foundations
Condominium units in projects meeting VA approval standards, though financing the construction of individual condo units is rare
Properties you won’t occupy as primary residences don’t qualify, including:
- Investment properties built specifically for rental income
- Vacation homes used seasonally rather than year-round
- Properties with commercial use exceeding allowable thresholds
- Second homes where you already maintain a primary residence elsewhere
Property features and restrictions:
The property must serve as your primary residence and cannot include income-producing features like:
- Rental units or accessory dwelling units designed for separate occupancy
- Commercial facilities such as home-based business spaces open to public traffic
- Farm operations generating substantial agricultural income
The property must meet VA’s modest size and amenity standards, focusing on safe, comfortable housing rather than luxury features or excessive square footage beyond area norms.
How Long Does VA Construction Loan Approval Take?
What timeline should borrowers expect for VA construction loan processing?
VA construction loan timelines vary based on project complexity and documentation completeness:
Planning and preparation – 4-8 weeks to:
- Select and potentially purchase land
- Choose qualified builder
- Finalize construction plans and specifications
- Obtain cost estimates and timeline projections
Application and approval – 6-12 weeks for:
- Application submission and initial review
- Documentation verification and builder vetting
- Appraisal based on projected completed value
- Underwriting review and conditional approval
- Condition clearing and final approval
Closing preparation – 1-2 weeks for:
- Title work and insurance arrangements
- Final document preparation
- Closing coordination and scheduling
Total timeline from initial planning to construction commencement typically ranges from 90-120 days, though complex projects or documentation issues may extend this period. Starting the process early and maintaining organized records accelerates approval.
What Credit Score Do You Need for VA Construction Loans?
VA construction loans don’t mandate specific minimum credit scores, but most lenders prefer scores above 620-640 for streamlined processing. Construction financing typically requires slightly higher credit standards than standard VA purchase loans due to added complexity and extended timelines.
Factors that strengthen applications:
- Demonstrated history of timely housing payments over the past 12-24 months
- Stable employment and income comfortably supporting projected housing expenses
- Reasonable debt obligations leaving adequate residual income
- Explanations for any past credit issues with evidence of resolution
- Strong financial reserves beyond minimum requirements
Even with qualifying credit scores, lenders examine complete credit profiles including payment patterns, debt levels, and recent credit activity to assess overall creditworthiness and capacity to manage construction project oversight.
Can Self-Employed Veterans Qualify for VA Construction Loans?
Yes. Self-employed veterans and service members can qualify for VA construction loans using documentation including:
- Two years of business tax returns showing income trends
- Year-to-date profit and loss statements if applying during the current tax year
- Business bank statements demonstrating regular deposits and cash flow
- CPA-prepared financial statements for complex business structures
- Business licenses and documentation proving ongoing operations
Lenders analyze self-employment income carefully, often averaging earnings across multiple years to account for natural business fluctuations. Stable or increasing income trends strengthen applications, while declining patterns may require additional explanation or documentation.
For alternative self-employment financing options:
- Bank Statement Loan – Uses business bank deposits instead of tax returns
- 1099 Loan – Qualifies independent contractors using 1099 income documentation
- P&L Loan – Approves based on CPA-prepared profit and loss statements
What Happens If Construction Takes Longer Than Expected?
How do lenders handle construction delays?
Construction delays occur regularly due to weather, material shortages, permitting issues, labor shortages, or contractor scheduling conflicts. VA construction loans typically allow 12 months for project completion, but lenders can grant extensions for justified delays.
Extension requests require:
- Written explanation of delay causes and circumstances beyond contractor control
- Updated construction timeline with realistic completion projections
- Verification that the builder remains financially stable and committed to project completion
- Confirmation that any material or design changes don’t significantly alter the approved project scope
- Lender inspection confirming work quality remains acceptable and project is progressing
Most lenders accommodate reasonable extensions without penalties, recognizing that construction timelines rarely proceed exactly as planned. However, excessive delays or evidence of contractor problems may trigger additional lender scrutiny or intervention to protect the loan.
During construction delays:
- Continue making interest-only payments on disbursed funds
- Maintain regular communication with your lender
- Document delay causes with photographs and written records
- Work with your builder to develop realistic revised timelines
- Address any issues promptly to prevent further complications
CHECKPOINT #1 – Re-reading REG Z compliance section…
VA Construction Loan Costs and Funding Fees
What costs should you expect with VA construction financing?
VA construction loans involve several cost categories spanning both the construction phase and permanent financing conversion.
Construction Phase Costs
Land acquisition – Purchase price if buying property as part of the construction loan
Site preparation – Clearing, grading, utility extensions, and foundation preparation
Construction materials and labor – All building costs for structure, systems, and finishes
Builder overhead and profit – Contractor margins built into construction pricing
Permit fees and inspections – Government charges for building permits and required inspections
Impact and connection fees – Utility connection charges and municipal impact fees
Construction contingency – Reserve amounts (typically a percentage of construction costs) for unforeseen expenses
Architecture and engineering – Design fees for plans, specifications, and engineering work
Surveys and testing – Property surveys, soil tests, and environmental assessments when required
Closing and Financing Costs
VA funding fee – One-time charge supporting the VA loan program (can be financed into loan amount)
Origination charges – Lender fees for processing and underwriting your construction loan
Appraisal fee – Cost of evaluating projected completed value based on plans and comparables
Title insurance – Protection for lenders and owners against title defects
Recording fees – Government charges for recording mortgage documents
Credit report – Cost of obtaining credit history
Flood certification – Verification of flood zone status
Construction loan administration – Fees for managing draw process and inspections during construction
VA Funding Fee for Construction Loans
The VA funding fee for construction loans follows the same structure as standard VA purchase loans, varying based on:
- Service category (regular military vs. Reserves/National Guard)
- Whether this is your first VA loan or subsequent use
- Your initial investment amount (larger contributions reduce the fee percentage)
Funding fee exemptions apply to:
- Veterans receiving VA disability compensation
- Veterans eligible for disability compensation but receiving retirement pay instead
- Surviving spouses receiving Dependency and Indemnity Compensation
- Service members awarded the Purple Heart
Check the VA funding fee chart for current amounts based on your specific circumstances.
Most borrowers finance the funding fee into their loan amount rather than paying at closing, spreading the cost over the loan life.
Interest During Construction
How do payments work during the construction phase?
During construction, you typically make interest-only payments based on funds disbursed to date. As construction progresses and additional draws release, interest payments increase proportionally. This structure minimizes carrying costs during construction when you’re not yet occupying the property.
Interest calculation details:
- Interest accrues daily on outstanding construction balances
- You make monthly interest-only payments on disbursed amounts
- The interest structure remains fixed from initial closing through permanent conversion
- Payment amounts increase with each construction draw as more funds disburse
After construction completes and the loan converts to permanent financing, payments transition to standard principal and interest payments over the remaining loan duration.
Advanced VA Construction Loan Topics
Can You Build on Land You Already Own?
How does existing land ownership affect VA construction financing?
Building on land you already own works well with VA construction loans. Your existing land equity doesn’t necessarily reduce financing amounts since VA loans offer flexible initial investment options. However, the land must meet specific requirements:
Location requirements:
- In an area where you’ll establish primary residence
- Accessible via legal roads with adequate utility connections
- Zoned for residential use with all necessary building permits available
Property characteristics:
- Sized appropriately for proposed construction without excessive acreage
- Free of environmental hazards or contamination affecting habitability
- Suitable soil and terrain conditions for construction
- Clear title without liens or encumbrances that would impair financing
Documentation needs: If you purchased land recently, lenders may require:
- Documentation showing acquisition price and payment source
- Verification that the land value aligns with appraisal expectations
- Proof of ownership through recorded deed
- Title insurance showing clear ownership
Land you’ve owned for extended periods typically requires less documentation, though lenders still verify clear title and suitability for construction.
How Do Construction Draws and Inspections Work?
What is the process for releasing construction funds?
VA construction loans release funds through a structured draw schedule tied to construction milestones. This process protects both borrowers and lenders by ensuring funds release only as work progresses satisfactorily.
Draw request submission:
- Builder completes work to a predetermined milestone
- Builder submits draw request with supporting invoices and lien waivers
- Lender schedules inspection to verify completed work
Inspection process:
- Lender-appointed inspector visits the construction site
- Inspector verifies work quality and completion percentage
- Inspector confirms work matches plans and specifications
- Inspector photographs and documents completed work
- Inspector submits report to lender recommending draw approval or noting issues
Fund disbursement:
- Lender reviews inspection report
- If approved, lender processes draw payment
- Funds typically release within 3-7 business days after approved inspection
- Payment goes directly to builder or into escrow for distribution
Common draw schedule milestones:
- Foundation completion
- Framing and roof installation (dried-in stage)
- Rough mechanical systems completion
- Drywall and interior finishes
- Final completion and occupancy readiness
The number of draws varies by project complexity and lender policies, typically ranging from 4-6 draws for most residential construction projects.
What Happens If the Builder Abandons the Project?
How are borrowers protected if contractors fail to complete construction?
Builder abandonment represents a serious concern, though proper contractor vetting minimizes this risk. If a builder abandons a VA construction project:
Immediate actions required:
- Notify your lender immediately about the situation
- Document all completed work with photographs and written descriptions
- Secure the construction site to prevent vandalism, theft, or weather damage
- Obtain lien releases for any completed work and materials already paid for
- Preserve all contracts, invoices, and payment records
Resolution options available:
- Hire a new qualified builder to complete remaining work using remaining construction funds
- Negotiate with the original builder (or bonding company if bonded) to complete the project or transfer responsibilities
- File insurance claims if the builder carried performance bonds or completion guarantees
- Pursue legal remedies against the builder for breach of contract and damages
Lender involvement:
Your lender will work with you to:
- Assess completed work and remaining construction needs
- Determine available remaining construction funds
- Evaluate options for project completion
- Potentially adjust the construction loan terms to accommodate new contractor
- Protect both your interests and the lender’s security in the project
Having adequate construction contingency reserves provides flexibility for addressing unexpected complications including builder issues. Additionally, selecting well-capitalized, experienced builders with strong track records significantly reduces abandonment risk.
Can You Make Changes During Construction?
What flexibility exists for modifying construction plans after approval?
Changes during construction are common, but the type and extent of modifications determine whether additional lender approval is required:
Minor changes typically permitted without additional approval:
- Material substitutions of equivalent quality and value
- Fixture selections within approved budget allowances
- Color choices and decorative elements
- Landscape details and exterior finishes
- Interior layout tweaks not affecting structural elements
Major changes requiring lender review and approval:
- Square footage modifications affecting appraised value
- Structural changes altering the approved floor plan
- Budget increases exceeding available contingency reserves
- Material upgrades significantly increasing project costs
- Changes affecting building permits or code compliance
- Modifications to foundation or structural systems
Before making any substantial changes:
- Discuss them with your builder to understand cost and timeline implications
- Contact your lender to determine whether approval is required
- Obtain written change orders documenting modifications and cost adjustments
- Ensure changes don’t delay construction beyond approved timelines
- Verify changes won’t negatively impact appraised value
Unauthorized significant changes may delay conversion to permanent financing, require additional appraisal reviews, or create complications with final inspections and occupancy certification.
Can You Act as Your Own General Contractor?
Do VA construction loans allow owner-builder arrangements?
VA construction loans generally don’t permit owner-builder arrangements where borrowers serve as their own general contractors. The VA requires licensed, qualified builders to manage construction projects to ensure:
- Professional construction management and quality control
- Proper licensing and insurance coverage
- Financial stability to complete projects
- Experience managing construction timelines and subcontractors
- Protection for both veterans and the VA against project failures
Limited exceptions may exist for:
- Veterans with professional construction licensing and experience
- Situations where the veteran can demonstrate construction qualifications equivalent to professional builders
- Markets where qualified builders are unavailable (extremely rare)
Even in these exceptional cases, lenders impose strict requirements including:
- Proof of construction licensing appropriate for the project scope
- Adequate insurance coverage including liability and workers compensation
- Demonstrated construction experience with successful completed projects
- Financial capacity to manage construction cash flow
- Detailed construction plans and realistic timelines
Most veterans find working with qualified professional builders provides better results, reduces stress, and ensures projects complete successfully within approved timelines.
What Documentation Do You Need for VA Construction Loans?
What paperwork is required for VA construction financing applications?
Comprehensive documentation requirements include:
Personal financial documents:
- Two years of federal tax returns with all schedules
- Recent pay stubs covering 30-60 days for employed applicants
- W-2 forms from the past two years
- Bank statements from all accounts spanning 60 days
- Retirement account statements if using for reserves
- Documentation of any other income sources
Self-employment documentation (if applicable):
- Two years of business tax returns including all schedules
- Year-to-date profit and loss statements
- Business bank statements
- CPA-prepared financials for complex businesses
- Business licenses and documentation of ongoing operations
Military service documentation:
- Certificate of Eligibility (COE)
- DD Form 214 for veterans or Statement of Service for active duty
- Proof of current military status if applicable
Property and construction documents:
- Complete architectural plans with floor layouts, elevations, and specifications
- Detailed construction specifications covering materials and methods
- Itemized cost breakdown from builder showing all expenses
- Construction timeline with milestone schedule
- Land documentation (deed if owned, purchase agreement if buying)
- Property survey showing boundaries and easements
- Soil tests and engineering reports if required by local conditions
- Building permits or evidence of permit applications
Builder qualification documents:
- Builder’s license copies
- Insurance certificates (general liability, workers compensation)
- Builder’s financial references or statements
- References from previous clients
- Portfolio of completed projects
Credit and identity verification:
- Valid government-issued identification
- Social Security cards for all applicants
- Authorization for credit report inquiries
- Written explanations for any credit issues or irregularities
Organized, complete documentation accelerates the approval process and reduces delays from missing information or unclear circumstances.
Explore all loan programs to understand your complete range of options.
Final VA Construction Loan Questions
Can You Finance Modular Home Construction With VA Loans?
Does VA construction financing cover factory-built housing?
VA construction loans can finance modular homes built to local building codes and permanently affixed to foundations. Key requirements include:
Modular homes must:
- Be constructed to local building codes, not just HUD manufactured home standards
- Be built in sections and assembled on-site on permanent foundations
- Be titled as real property, not personal property
- Demonstrate quality and permanence comparable to site-built construction
- Meet all VA minimum property requirements
Manufactured homes built solely to HUD code typically don’t qualify for VA construction loans—they require specialized manufactured home financing programs with different requirements and structures.
If considering modular construction:
- Verify with your lender that the specific building system and manufacturer meet VA requirements
- Ensure the modular home will be titled as real property
- Confirm permanent foundation meeting local codes
- Obtain documentation showing the home meets local building codes beyond just HUD standards
Modular construction can offer cost savings and faster construction timelines compared to traditional site-built homes while still qualifying for VA construction financing.
How Does VA Construction Financing Compare to Other Options?
What alternatives exist to VA construction loans?
Different construction financing options suit different borrower circumstances:
Conventional construction loans:
- Require substantial initial investments
- Impose no income limits
- May offer faster processing in some markets
- Suitable for those building in any location without geographic restrictions
- Often require stronger credit and financial profiles
FHA construction-to-permanent loans:
- Offer flexible funding structures with competitive terms
- Include mortgage insurance increasing overall costs
- Serve borrowers who don’t qualify for VA benefits
- Have property limits and specific FHA requirements
USDA construction loans:
- Provide competitive terms for rural property construction
- Restrict eligibility to properties in USDA-designated areas
- Impose income limits based on area median income
- Offer flexible initial investment options similar to VA loans
Local bank construction loans:
- May offer competitive terms in specific markets
- Provide flexibility for unique situations
- Often require substantial initial investments
- Typically involve two closings (construction, then permanent)
VA construction loans typically provide the best overall value for eligible military families due to:
- Competitive structures without private mortgage insurance
- Flexible initial investment options
- Single-close convenience
- Builder flexibility
- Streamlined processing for qualified veterans
Each option presents distinct advantages and limitations. Your optimal choice depends on military eligibility, property location, construction timeline, builder relationships, and personal financial circumstances.
What Are Common Reasons for VA Construction Loan Denial?
Why do VA construction loan applications get rejected?
Understanding common denial reasons helps applicants avoid preventable issues:
Builder disqualification:
- Contractor lacks proper licensing or insurance
- Builder has poor financial standing or credit issues
- Insufficient construction experience or poor references
- History of incomplete projects or legal disputes
Inadequate construction plans:
- Incomplete architectural drawings or specifications
- Unrealistic budgets that don’t align with market costs
- Designs exceeding VA modest housing standards
- Plans not meeting local building codes
Financial qualification issues:
- Insufficient income to support proposed housing expenses
- Excessive debt obligations consuming too much income
- Inadequate residual income per VA requirements
- Insufficient reserves for closing costs and contingencies
Property problems:
- Land located where borrower won’t establish primary residence
- Property with access issues, environmental problems, or zoning restrictions
- Excessive acreage beyond reasonable residential needs
- Land values not supporting total construction costs
Credit concerns:
- Recent serious delinquencies without acceptable explanations
- Insufficient credit history to assess creditworthiness
- Unstable employment or declining income trends
- Recent bankruptcies or foreclosures within waiting periods
Military eligibility issues:
- Service doesn’t meet minimum duration requirements
- Discharge characterization not acceptable
- Certificate of Eligibility cannot be obtained
Addressing these areas proactively before applying significantly increases approval probability and reduces processing delays. Working with experienced VA construction lenders helps navigate requirements and position your application for success.
Can National Guard and Reserve Members Use VA Construction Loans?
What requirements apply to Guard and Reserve members for construction financing?
Yes, National Guard and Reserve members qualify for VA construction loans after completing six years of service. Requirements include:
Active Reserve or Guard service including:
- Attending required monthly drill periods
- Completing annual training requirements
- Maintaining satisfactory participation records
- Receiving honorable characterization of service
Alternative qualification paths:
- Active duty service for qualifying periods
- Deployment to active duty during wartime or contingency operations
- Service-connected disability discharge at any point
Guard and Reserve members obtain Certificates of Eligibility using DD Form 214 plus points statements showing total qualifying service time. The construction loan process follows the same procedures as for other eligible service members once military qualification is established.
How Does Divorce Affect VA Construction Loans?
What happens if divorce occurs during construction or after completing the home?
Divorce complicates VA construction loans in several ways:
During construction:
- Both spouses remain legally obligated on the loan
- Divorce decrees don’t override mortgage contract obligations
- The VA remains liable based on original loan terms
- Construction must continue with both borrowers committed
Resolution options:
- Complete construction as planned – Both parties remain on the loan until construction finishes, then address the property in divorce settlement
- One spouse continues alone – May require refinancing if lender permits and qualifying spouse meets income requirements alone
- Cancel construction – Extremely difficult and costly, involving unwinding the loan and potentially losing deposits and land
After construction completes:
Standard VA loan divorce considerations apply:
- Refinance to remove one spouse using a new VA loan or conventional financing
- Sell the property to satisfy joint obligations
- One spouse assumes the loan if lender allows and qualifies independently
- Continue co-borrowing despite divorce (creates ongoing entanglement)
Entitlement considerations:
If your ex-spouse keeps a home financed with your joint VA construction loan, your entitlement may remain tied to that property until:
- The property sells and loan pays off
- Your ex-spouse refinances into their own financing
- You request substitution of entitlement (complex process)
Consult with both your divorce attorney and mortgage professionals to understand implications and develop the best strategy for your circumstances.
Can You Use VA Construction Loans for Additions or Renovations?
Do VA construction loans finance major home improvements?
VA construction loans specifically finance new construction projects, not additions or renovations to existing homes. For substantial improvements to existing properties, consider:
VA renovation loans that combine purchase price and renovation costs:
- Finance properties needing repairs or improvements
- Include renovation costs in the mortgage
- Provide single-close convenience similar to construction loans
- Work with existing structures rather than new builds
VA cash-out refinances for properties you already own:
- Access equity to fund improvements
- Refinance existing mortgages while pulling out cash for renovations
- Maintain competitive VA loan terms and benefits
View VA cash-out refinance case studies to understand equity access for improvements.
Home equity lines of credit (HELOCs):
- Borrow against existing equity as needed
- Pay interest only on amounts used
- Flexible access for ongoing or phased improvements
The VA construction loan specifically serves veterans building new homes from the ground up, while other programs better address renovation and improvement needs for existing properties.
Ready to get started? Apply now or schedule a call to discuss your situation.
Alternative Loan Programs for Construction and Military Families
If a VA construction loan isn’t the right fit, consider these alternatives:
- VA Loan – Standard VA financing for purchasing existing homes without construction components
- USDA Construction Loan – Rural construction financing with competitive terms for properties in USDA-eligible areas
- FHA Loan – Flexible government-backed financing with various initial investment options for existing or new construction homes
- Conventional Construction Loan – Traditional construction financing for borrowers building outside military benefits or in any location
- Renovation Loan – Combined purchase and improvement financing for properties needing repairs or upgrades
Explore all 30+ loan programs to find your best option.
Not sure which program is right for you? Take our discovery quiz to find your path.
Helpful VA Construction Loan Resources
Official VA Construction Guidance
VA Home Loans Overview and Programs – Comprehensive Department of Veterans Affairs resource explaining all loan programs including construction financing, eligibility requirements, and program benefits for military families.
VA Builder Requirements and Standards – Official VA guidance on contractor qualifications, licensing, insurance, and financial stability standards for construction projects.
VA Minimum Property Requirements – Detailed property standards covering construction quality, safety requirements, and minimum acceptable property characteristics for VA-financed homes.
VA Funding Fee Chart and Exemptions – Current funding fee schedules for all VA loan types including construction financing, showing amounts based on service type and initial investment levels.
Construction and Building Standards
HUD Construction Requirements Overview – Federal housing construction standards covering minimum property requirements, inspection protocols, and quality benchmarks applicable to government-backed construction financing.
International Code Council Building Codes – Professional organization publishing model building codes adopted by most U.S. jurisdictions, providing standards for residential construction safety and quality.
National Association of Home Builders Resources – Trade association representing residential construction industry professionals, offering consumer resources about building processes, contractor selection, and construction best practices.
Military and Veteran Resources
VA Loan Eligibility Requirements – Official eligibility criteria detailing service requirements for active duty members, veterans, National Guard, Reserves, and surviving spouses.
VA Certificate of Eligibility Application – Online portal for veterans to obtain Certificates of Eligibility electronically through the eBenefits system.
Military OneSource Financial Resources – Department of Defense program offering free financial counseling, education, and resources specifically for military families navigating construction projects and mortgages.
Educational and Consumer Resources
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau Mortgage Guide – Federal consumer protection agency providing unbiased information about mortgage financing, closing processes, and borrower rights for all loan types.
HUD Housing Counseling Services – Directory of HUD-approved housing counselors offering free or low-cost assistance with mortgage questions, financial planning, and homeownership education.
Need a Pre-Approval Letter—Fast?
Buying a home soon? Complete our short form and we’ll connect you with the best loan options for your target property and financial situation—fast.
- Only 2 minutes to complete
- Quick turnaround on pre-approval
- No credit score impact
Got a Few Questions First?
Not Sure About Your Next Step?
Skip the guesswork. Take our quick Discovery Quiz to uncover your top financial priorities, so we can guide you toward the wealth-building strategies that fit your life.
- Takes just 5 minutes
- Tailored results based on your answers
- No credit check required
Related Posts
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get program updates and rate insights in your inbox.