Foreign National Loan: 7 Essential Steps to Purchase U.S. Real Estate Without U.S. Credit

How a Foreign National Loan Enables International Buyers to Invest in U.S. Property
International buyers seeking U.S. real estate face qualification barriers when traditional lenders require Social Security numbers, U.S. credit history, and domestic income verification. Foreign national loans evaluate your qualification using international credit profiles, offshore income, and alternative documentation. Whether you’re purchasing a vacation property, investment real estate, or establishing a U.S. residence, this specialized financing recognizes your financial strength regardless of citizenship or residency status.
Key Details: What You’ll Learn About Foreign National Loans
- A foreign national loan provides mortgage financing specifically designed for non-U.S. citizens and non-residents purchasing American real estate without U.S. credit history, Social Security numbers, or domestic income documentation (Federal Reserve international real estate investment data)
- International buyers from any country can qualify using foreign income documentation, international credit reports, and passport identification rather than traditional U.S. verification methods (IRS foreign national tax requirements)
- Property types including single-family homes, condominiums, multi-unit buildings, and investment properties qualify when borrowers meet foreign national lending criteria
- Qualification focuses on demonstrating financial capacity through international bank statements, foreign income verification, and liquid asset documentation rather than U.S. employment or credit bureau reporting
- A foreign national loan typically requires equity contributions reflecting international buyer risk profiles and currency exchange considerations
- Primary residences, vacation homes, and investment properties all qualify under various foreign national program structures with appropriate documentation and intended use verification
- Processing accommodates international time zones, foreign language documents with certified translations, and cross-border fund transfers through specialized underwriting teams experienced with international transactions (CFPB foreign national mortgage information)
Ready to explore your options? Schedule a call with a loan advisor.
What Is a Foreign National Loan?
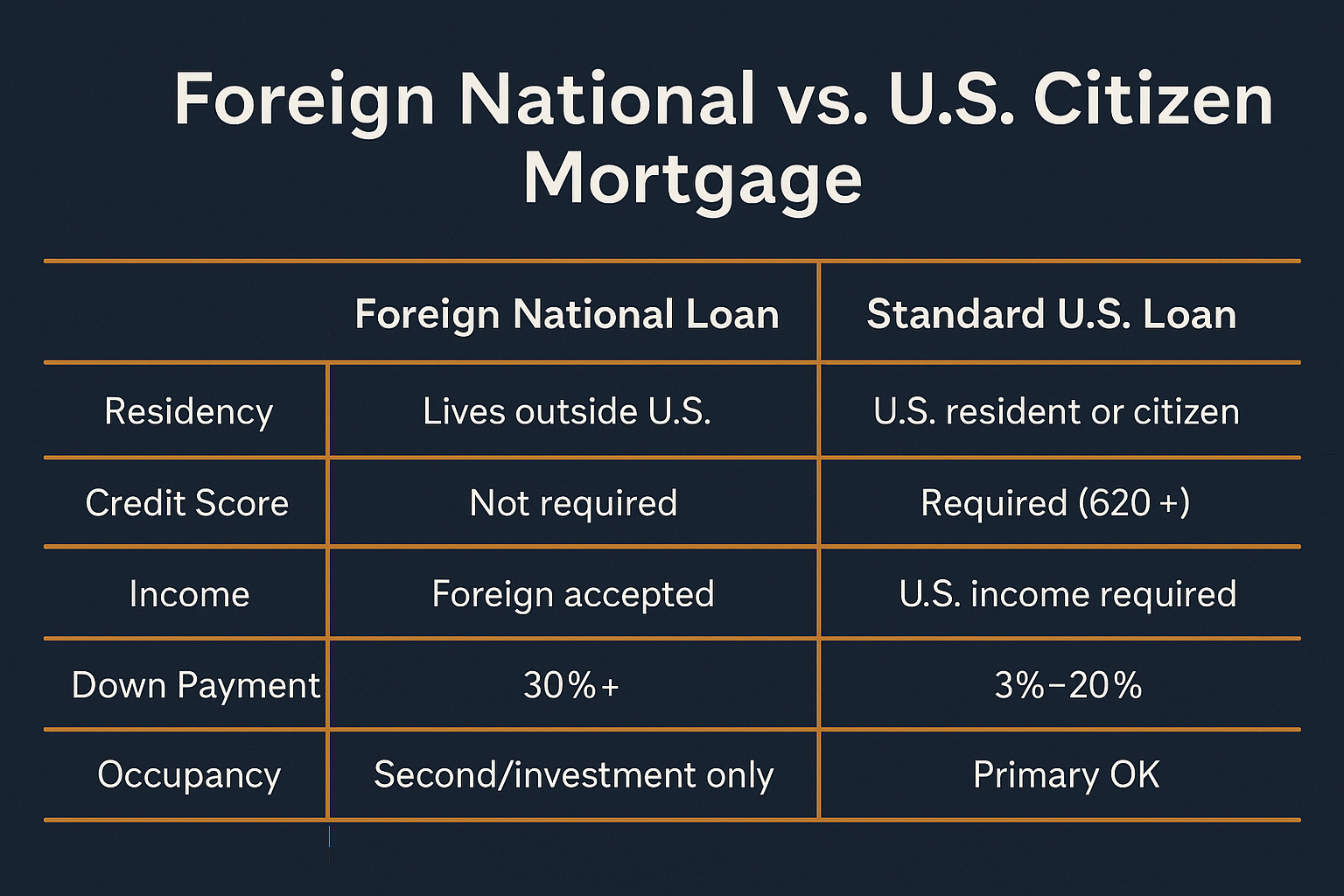
A foreign national loan represents specialized mortgage financing designed for international buyers—individuals who are not U.S. citizens or permanent residents—purchasing American real estate. These programs accommodate the unique documentation, verification, and qualification challenges that international buyers face when conventional mortgage programs require U.S.-specific documentation like Social Security numbers, domestic credit histories, and U.S. employment verification.
How does a foreign national loan work? Lenders structure qualification around alternative documentation methods recognizing that international buyers lack U.S. credit histories, domestic employment, or traditional verification touchpoints that standard mortgages require. Instead, programs accept international bank statements, foreign income documentation, passport identification, and overseas credit reports when available, evaluating creditworthiness through alternative means demonstrating financial capacity and reliability.
The structure acknowledges that millions of international investors and relocating professionals seek U.S. property ownership for investment diversification, vacation home purposes, relocation preparation, or family member accommodation despite lacking access to traditional U.S. mortgage products. Rather than requiring impossible U.S.-specific documentation, foreign national loan programs evaluate financial capability through internationally-focused verification methods.
A foreign national loan serves various populations including international investors diversifying portfolios into U.S. real estate, foreign professionals relocating to America for work, international students or their families purchasing homes for education periods, and global citizens acquiring U.S. vacation properties or family residences.
Who Benefits Most from a Foreign National Loan?
Several borrower profiles find exceptional value in foreign national loan structures. These programs serve international individuals whose citizenship or residency status prevents traditional U.S. mortgage qualification but who possess financial capacity for American property ownership.
International real estate investors seeking U.S. property portfolio diversification represent primary foreign national loan candidates. If you’re based overseas but recognize U.S. real estate’s investment potential—stable property rights, transparent markets, potential appreciation, and rental income opportunities—foreign national financing enables acquiring American properties without U.S. residency or citizenship.
Foreign professionals relocating to the United States for employment commonly purchase homes before establishing U.S. credit or employment history. Foreign national loans enable property acquisition aligned with relocation timelines rather than waiting years to build domestic credit and verification touchpoints conventional mortgages demand.
International families with children attending U.S. universities often purchase properties for student housing during education periods. Rather than paying rent throughout college years, families invest in properties their children occupy, potentially generating rental income from roommates and building equity during the education period.
Global citizens maintaining international primary residences but desiring U.S. vacation homes, seasonal residences, or family gathering properties use foreign national financing to acquire American real estate while remaining based overseas without U.S. residency status changes.
Wealthy international individuals seeking safe haven assets, currency diversification, or real estate portfolio geographic distribution find U.S. property ownership provides stability, strong property rights, and investment security that some international markets cannot match.
Explore all loan programs to understand your full range of options.
What Are the Requirements for a Foreign National Loan?
Understanding the specific qualification criteria helps you assess whether a foreign national loan fits your international investment or relocation situation. While requirements vary between lenders, certain standards commonly apply across most foreign national programs.
Valid passport identification – All foreign national loan programs require valid passports from your country of citizenship establishing identity and nationality. Additional government-issued identification from your home country strengthens applications.
Equity contribution expectations – Foreign national loans typically require larger initial equity contributions compared to traditional U.S. mortgages, commonly ranging based on property type, occupancy intention, and borrower profile strength. Higher equity compensates for international borrower considerations including cross-border enforcement complexity and currency risk factors.
Income documentation from foreign sources – Programs accommodate various income verification methods recognizing international employment diversity:
- Foreign employment letters from overseas employers
- International bank statements showing regular income deposits
- Foreign country tax returns when available
- Business ownership documentation from overseas companies
- Investment income or passive income verification
- Asset-based qualification using liquid holdings
International bank statements – Bank statements from your home country financial institutions covering multiple months demonstrate financial management capability, cash reserves, and fund sources for property purchases. Statements require certified English translations when in foreign languages.
Credit documentation – While U.S. credit histories don’t exist for international buyers, some countries maintain credit bureaus providing reports similar to U.S. systems. Where available, international credit reports strengthen applications. Countries without formalized credit reporting rely more heavily on bank statements and reference letters demonstrating financial responsibility.
Property occupancy intentions – Clear documentation regarding property use—primary residence, vacation home, or investment rental—affects program selection and requirements. Investment properties typically require larger equity contributions than primary or vacation residences.
U.S. address or contact information – Lenders need reliable U.S.-based communication methods during loan processing. While you need not reside in America currently, establishing U.S. mail forwarding, phone numbers, or authorized representative relationships facilitates communication.
Source of funds documentation – All funds for equity contributions and closing costs require documentation showing legitimate sources. International wire transfer documentation, foreign bank account statements showing fund accumulation, and explanations of fund origins satisfy anti-money laundering compliance requirements.
How Does a Foreign National Loan Differ from Traditional U.S. Mortgages?
The fundamental distinction lies in the identification and documentation methods accommodating international buyers lacking U.S.-specific verification touchpoints. Understanding these differences helps you prepare appropriate documentation and set realistic expectations.
Traditional U.S. mortgage characteristics:
- Social Security number required for credit reporting
- U.S. credit history from major bureaus
- Domestic employment with W-2 or traditional tax documentation
- U.S. bank accounts and financial institution relationships
- Standard verification through U.S. databases and systems
- Modest equity requirements for qualified borrowers
Foreign national loan characteristics:
- Passport identification substitutes for Social Security numbers
- International credit reports or alternative credit assessment
- Foreign income documentation from overseas employment
- International bank accounts with translated statements
- Manual underwriting accommodating foreign documentation
- Larger equity contributions reflecting international considerations
Qualification methodology differences:
- Traditional mortgages leverage automated verification systems
- Foreign national loans require manual underwriting with human review
- U.S. mortgages access extensive database verification
- Foreign national financing relies on document authenticity assessment
- Traditional programs assume U.S. legal framework familiarity
- International programs accommodate cross-border legal complexities
Why are equity requirements higher for foreign national loans? Larger equity contributions offset several factors including enforcement complexity across international borders, currency exchange risk if foreign income serves U.S. obligations, limited credit history verification in some countries, and higher perceived risk from alternative documentation methods. The additional equity investment provides security cushions justifying lenders’ specialized international lending programs.
Ready to discuss your purchase scenario? Submit a purchase inquiry to explore your options.
What Property Types Qualify for a Foreign National Loan?
A foreign national loan program accommodates various property categories serving diverse international buyer purposes. Understanding eligibility helps you identify appropriate U.S. real estate opportunities.
Eligible property types:
- Single-family detached homes for various uses
- Condominiums in approved developments
- Townhomes and row houses
- Multi-unit properties (2-4 units) for investment
- Vacation homes and seasonal properties
- Investment properties for rental income
- New construction and resale properties
Can you purchase investment properties with foreign national loans? Yes, unlike some U.S. mortgage programs restricting to owner-occupants, foreign national loans accommodate investment property purchases enabling international investors to acquire American rental properties. Investment properties typically require larger equity contributions than properties you’ll occupy personally.
What about vacation homes? Vacation property purchases for personal seasonal use qualify under foreign national programs with documentation showing property use intentions. Vacation homes typically require equity contributions between primary residences and pure investment properties, reflecting the limited occupancy patterns.
Are there property location restrictions? Foreign national loan availability concentrates in markets with significant international buyer activity including major metropolitan areas, vacation destinations, university towns, and markets with substantial foreign investment interest. Rural properties or small markets with minimal international buyer presence may have limited program availability.
Can you purchase luxury properties? High-value properties qualify for foreign national financing through lenders specializing in luxury real estate. Jumbo foreign national loan programs accommodate property values exceeding standard conforming limits, serving international buyers seeking premium American real estate.
See how other foreign nationals have successfully used this financing:
How Do You Document Income Without U.S. Employment?
Understanding income verification methods helps you prepare appropriate documentation demonstrating payment capacity without traditional U.S. employment verification. Foreign national programs accommodate diverse international income sources through alternative verification.
Foreign employment documentation – Employment letters from overseas employers detailing position, tenure, compensation, and employment stability provide primary income verification. These letters require notarization or official company letterhead with contact information for verification.
International bank statements – Bank statements from foreign financial institutions showing regular deposits establishing income patterns serve as powerful verification. Statements covering 6-24 months demonstrate income consistency and financial management capability.
Foreign tax returns – When your country maintains tax systems documenting income, translated tax returns provide official income verification. Many countries lack U.S.-style annual tax filing, making tax returns unavailable—alternative documentation then substitutes.
Business ownership documentation – International business owners provide company registration documents, financial statements, ownership verification, and evidence of distributions or salary supporting personal income claims.
Investment income verification – Passive income from investments, rental properties, or business interests requires documentation showing income sources, payment amounts, and income reliability through financial statements or bank deposits.
Asset-based qualification – Some foreign national programs emphasize liquid asset holdings over income, qualifying borrowers based on substantial bank balances, investment portfolios, or other liquid assets rather than monthly income flow. This approach suits ultra-high-net-worth international buyers.
What if you’re paid in foreign currency? Income in foreign currencies requires addressing exchange rate considerations. Lenders evaluate income stability in U.S. dollar terms, potentially requiring higher income cushions accounting for currency fluctuation risk when foreign income serves U.S. mortgage obligations.
How do you verify self-employment income internationally? Self-employed international borrowers provide business registration, bank statements showing business income deposits, client contracts or invoices, and business financial statements when available. The verification focuses on demonstrating stable business income through bank deposits rather than requiring formalized books like U.S. CPAs maintain.
Calculate your foreign national loan scenarios:
What Documentation Does a Foreign National Loan Require?
Understanding the specific documentation requirements helps you prepare for foreign national loan applications. The documentation differs from traditional U.S. mortgages while accomplishing similar verification objectives through internationally-focused methods.
Required documentation typically includes:
- Valid passport from country of citizenship
- Additional government identification from home country
- International bank statements (6-24 months with translations)
- Foreign employment letters or income verification
- Foreign tax returns when applicable (with translations)
- International credit reports where available
- Proof of funds for equity contribution and reserves
- Property purchase contract
- U.S. property appraisal
- Source of funds documentation
- Wire transfer instructions for international funds
- Contact information and U.S. communication methods
How do document translations work? Non-English documents require certified translations by qualified professional translators. Translation services specializing in financial documents understand terminology and formatting lenders expect. Translators certify accuracy and attach original language documents alongside English versions.
What about countries without credit bureaus? Many countries lack formalized credit reporting systems like U.S. credit bureaus maintain. Alternative credit documentation then includes utility payment records, reference letters from banks, rental payment history, or other evidence demonstrating financial responsibility and payment reliability.
Do you need U.S. tax identification numbers? While not required for loan approval, foreign nationals purchasing U.S. real estate eventually need Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers (ITINs) or Social Security numbers (if eligible) for U.S. tax reporting obligations related to property ownership, rental income, or eventual property sales. Consult tax professionals about proper identification and reporting.
How do you prove fund sources for anti-money laundering compliance? All funds for property purchases require documentation showing legitimate origins. Acceptable documentation includes foreign bank statements showing fund accumulation over time, documentation of property sales or business sales generating funds, inheritance documentation, or other legitimate source explanations with supporting evidence.
Are there special requirements for specific countries? Some countries face enhanced scrutiny due to money laundering concerns, sanctions, or international relations considerations. Borrowers from these countries may face additional documentation requirements, longer processing times, or limited lender availability. However, most countries maintain normal processing without special restrictions.
Common Foreign National Loan Questions
Can you get a foreign national loan from any country?
Most countries enable their citizens to pursue U.S. property ownership through foreign national loan programs. However, countries under U.S. sanctions, designated as high-risk for money laundering, or lacking diplomatic relations with America may face restrictions or require specialized lenders with international compliance expertise.
The vast majority of international buyers from developed and developing nations face no country-specific prohibitions, accessing foreign national financing through documentation and verification appropriate to their home countries.
What if your country uses a different currency?
Foreign currency income and assets are universal among foreign national borrowers. Lenders accommodate currency diversity by converting foreign currency amounts to U.S. dollars using current exchange rates, evaluating income sufficiency and asset adequacy in dollar terms.
Currency considerations include:
- Exchange rate fluctuations affecting income value
- Potential requirement for higher income cushions
- Currency conversion documentation for fund transfers
- Exchange rate timing for closing fund transfers
- Currency risk factors in lender underwriting
Can you refinance foreign national loans later?
Yes, refinancing foreign national loans into better terms as circumstances improve represents a common strategy. If you obtain permanent resident status or citizenship enabling traditional financing, refinancing into conventional or government-backed programs may provide better rates and terms. Even maintaining foreign national status, refinancing into improved foreign national programs as property equity grows provides access to better pricing.
Some borrowers use foreign national financing initially, planning eventual refinancing as U.S. residency status evolves or property values appreciate creating more favorable equity positions.
What if you can’t make mortgage payments from abroad?
Payment difficulties affect foreign national borrowers similarly to domestic borrowers. However, international distance complicates communication and resolution. Strategies for managing payment challenges include establishing U.S. bank accounts enabling automatic payments, authorizing U.S.-based representatives to manage property and financial matters, and maintaining open communication with lenders when difficulties arise.
Rental income from investment properties can cover obligations even when personal circumstances change. Property management companies handle day-to-day operations enabling continued property ownership despite international distance.
How Do Foreign National Loan Rates Compare to Traditional U.S. Mortgages?
Understanding the pricing framework helps you evaluate total financing costs for U.S. property purchases. Foreign national loan pricing typically reflects premiums compared to traditional domestic mortgage programs.
What factors influence foreign national loan pricing? Several elements affect your specific rate and fees:
- Country of citizenship and residence
- Equity contribution percentage
- Property type and intended use
- Loan amount relative to property value
- International credit documentation availability
- Income verification quality and source stability
- Overall financial profile strength including reserves
Are foreign national rates higher than conventional mortgages? Yes, foreign national financing typically carries rate premiums above comparable U.S. borrower programs—often ranging from modest to significant increases depending on borrower profile, property type, and program specifics. This premium reflects cross-border enforcement complexity, currency risk considerations, alternative documentation verification costs, and specialized underwriting requirements.
What about origination fees and closing costs? Foreign national loans often involve higher origination fees compared to traditional mortgages due to manual underwriting, international documentation review, translation costs, and specialized expertise requirements. Expect total closing costs to exceed standard domestic mortgage transactions.
Can you improve pricing through relationships or equity? Yes, larger equity contributions significantly improve pricing, demonstrated prior U.S. real estate ownership showing familiarity with American property markets, substantial liquid reserves beyond minimums, and countries with strong credit reporting and verification systems all access better pricing tiers.
How does property use affect pricing? Primary residences where you’ll live generally receive the best pricing, vacation homes carry moderate premiums, and investment properties typically face highest rates reflecting rental property risk factors and non-owner-occupancy considerations.
What Are the Advantages of a Foreign National Loan?
Understanding the specific benefits helps you evaluate whether pursuing U.S. property ownership through foreign national financing aligns with your international investment or relocation goals. A foreign national loan offers distinct advantages for international buyers.
Key advantages include:
U.S. property ownership without residency – Purchase American real estate while maintaining primary residency in your home country. You need not live in the U.S., obtain residency status, or change citizenship to own property, enabling international portfolio diversification without relocation.
Leverage international income and assets – Use foreign income, overseas employment, and international bank accounts to qualify rather than requiring impossible U.S. employment or domestic income documentation. Your global financial position supports U.S. property acquisition.
Portfolio geographic diversification – Add American real estate to investment portfolios concentrated in single countries or regions. U.S. property provides geographic diversification, currency diversification through dollar-denominated assets, and access to stable property markets with strong legal protections.
Vacation home or family property acquisition – Establish U.S. properties for family vacations, seasonal use, or accommodation during American visits without permanent relocation requirements. Create family gathering places or vacation retreats accessible during U.S. travels.
Investment property income generation – Acquire American rental properties generating dollar-denominated income streams. Real estate investors recognize U.S. rental markets’ income potential, appreciation prospects, and portfolio enhancement opportunities.
Student housing during education – Purchase properties for children attending U.S. universities rather than paying rent throughout education periods. Build equity during college years while providing quality housing, potentially generating rental income from roommates.
Alternative Loan Programs for International Buyers
If a foreign national loan isn’t the right fit, consider these alternatives:
- ITIN Loan – For non-citizens with Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers and U.S. credit history
- Asset-Based Loan – Leverage investment portfolios and liquid assets for qualification without traditional income documentation
- Bank Statement Loan – For self-employed foreign nationals with U.S. business operations and bank accounts
- DSCR Loan – For investment properties qualifying based on rental cash flow without personal income verification
- No-Doc Loan – Minimal documentation financing for foreign nationals with strong credit and substantial assets
Explore all 30+ loan programs to find your best option.
Not sure which program is right for you? Take our discovery quiz to find your path.
Advanced Foreign National Loan Questions
Can you purchase properties through business entities or trusts?
Many international buyers prefer purchasing U.S. properties through business entities (LLCs, corporations) or trusts for liability protection, estate planning, or tax optimization purposes. Foreign national programs accommodate entity ownership with appropriate documentation including:
- Entity formation documents and ownership verification
- Operating agreements or corporate bylaws
- Entity tax identification numbers
- Individual guarantees from entity beneficiaries
- Documentation of entity purpose and ownership structure
Consult with international tax attorneys about optimal ownership structures balancing U.S. tax obligations, home country tax treatment, estate planning considerations, and liability protection before finalizing entity strategies.
What visa types enable foreign national loan qualification?
Foreign national loans serve non-residents and non-permanent residents regardless of visa status or lack thereof. Common visa holders using foreign national financing include:
- H-1B and other work visa holders (though these may qualify for traditional mortgages)
- Student visa holders (F-1) or their families
- Tourist visa holders making investment purchases
- Individuals with no current U.S. visa planning future visits
- Temporary workers or expatriates on assignment
How do tax obligations work for foreign property owners?
U.S. property ownership triggers various tax obligations that international buyers must understand and plan for:
Rental income taxation – Foreign nationals earning U.S. rental income pay federal and potentially state income taxes on net rental profits. Tax treaties between the U.S. and your home country may affect tax rates or obligations.
Property tax obligations – All property owners pay local property taxes regardless of citizenship. These annual obligations continue as long as you own properties.
Sale proceeds taxation – Foreign nationals selling U.S. real estate face capital gains taxation on profits plus FIRPTA withholding (Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act) requiring buyers to withhold portions of purchase prices and remit to IRS.
Estate tax considerations – U.S. estate taxes may apply to foreign nationals’ U.S. property holdings upon death, though tax treaties and exemption amounts vary by country and situation.
Consult international tax professionals familiar with both U.S. tax law and your home country’s tax treatment of foreign real estate before purchasing American properties.
Can you use gift funds from family members abroad?
Yes, foreign national programs accept gift funds from family members for equity contributions, closing costs, or reserves. Gift documentation requirements include:
- Gift letters explaining relationships and confirming no repayment expectations
- Documentation of donors’ fund sources and capacity
- Wire transfer documentation showing fund movement from donors
- Donor identification and contact information
- Evidence funds originated from legitimate sources
International gift transfers face enhanced anti-money laundering scrutiny. Thorough documentation showing legitimate gift sources and family relationships satisfies compliance requirements.
What happens if currency exchange rates change significantly?
Currency fluctuations between loan application and closing can affect fund transfers for equity contributions. Significant currency movements may require additional funds when your home currency weakens against dollars, or result in excess funds when it strengthens.
Currency risk management strategies:
- Transfer funds early locking in favorable exchange rates
- Maintain U.S. dollar accounts minimizing conversion timing risk
- Budget cushions accounting for potential adverse movements
- Use forward contracts locking exchange rates for large transfers
- Monitor exchange rates during transaction periods
Can foreign nationals assume existing mortgages?
Mortgage assumption—taking over sellers’ existing mortgages—faces significant limitations for foreign nationals. Most conventional mortgages prohibit assumption or require full qualification meeting today’s standards. Government-backed loans (FHA, VA, USDA) may allow assumption but typically require U.S. citizenship or permanent residency.
Foreign nationals generally cannot assume existing mortgages, instead requiring new foreign national financing for property purchases.
How do foreign nationals establish U.S. credit history?
Building U.S. credit history enables eventual refinancing into traditional domestic mortgages with better terms. Strategies for establishing American credit include:
- Obtaining secured U.S. credit cards requiring deposits
- Adding as authorized users on U.S. credit cards
- Opening U.S. bank accounts and using them consistently
- Establishing utility accounts in your name at U.S. properties
- Applying for store credit cards or small credit facilities
- Maintaining perfect payment records on all U.S. obligations
Building strong U.S. credit typically requires 12-24 months of consistent payment history before traditional mortgage qualification becomes possible.
Can you purchase properties before relocating to the U.S.?
Yes, foreign national loans specifically enable property purchases before U.S. relocation, whether you plan eventual immigration or purchase properties for investment without relocation intentions. This advance purchasing provides several benefits:
- Secure housing before arrival avoiding rental markets
- Lock in property prices before relocation
- Begin building U.S. financial history and relationships
- Establish residency documentation for school enrollment
- Create familiarity with U.S. markets and processes
Many international professionals relocating for work purchase homes months before actual relocation, moving directly into owned properties rather than temporary housing.
What if political or economic changes affect your home country?
International political instability, economic crises, or currency collapses in home countries can affect foreign national borrowers’ payment capacity. U.S. property ownership provides asset protection and geographic diversification exactly for these scenarios.
If circumstances in your home country deteriorate, communicate with lenders about temporary payment arrangements, consider renting properties generating income covering obligations, or sell properties if necessary. The strong property rights and stable legal framework in America protect your assets regardless of home country developments.
How do foreign nationals handle property management from abroad?
Managing U.S. properties while residing internationally requires systems enabling remote oversight:
- Professional property management companies handling day-to-day operations
- Online payment systems automating rent collection and expense payments
- Digital communication maintaining renter and vendor relationships
- Periodic visits or authorized representatives conducting inspections
- Insurance coverage protecting against risks during absent periods
- Automated mortgage payments eliminating manual transaction needs
Property management companies particularly benefit international owners, handling leasing, maintenance, rent collection, and tenant issues for fees typically worth the convenience for distant owners.
Ready to get started? Apply now or schedule a call to discuss your situation.
Helpful Foreign National Loan Resources
Official Government Guidance:
Federal Reserve International Real Estate Investment Data – Federal Reserve research on foreign investment in U.S. residential real estate markets, international buyer trends, and cross-border property ownership patterns.
IRS Foreign National Tax Requirements – Internal Revenue Service comprehensive guidance on U.S. tax obligations for nonresident aliens including property ownership, rental income reporting, and sale proceeds taxation.
CFPB Foreign National Mortgage Information – Consumer Financial Protection Bureau guidance explaining mortgage access for non-U.S. citizens, qualification methods, and borrower protections for international property buyers.
Industry Organizations:
IRS ITIN Application Information – Internal Revenue Service resource on obtaining Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers required for foreign nationals’ U.S. tax compliance related to property ownership and income.
Treasury FIRPTA Information – Internal Revenue Service guidance on Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act withholding requirements affecting foreign nationals selling U.S. real estate.
Educational Resources:
State Department Visa Information – U.S. Department of State comprehensive visa information for foreign nationals including temporary visitor, work, and student visa categories that may correlate with U.S. property ownership.
HUD Fair Housing for Foreign Nationals – Department of Housing and Urban Development information on fair housing rights protecting foreign nationals from discrimination in U.S. real estate transactions and rental markets.
Need local expertise? Get introduced to trusted partners including loan officers, international tax advisors, and real estate professionals experienced with foreign buyers in your area.
Need a Pre-Approval Letter—Fast?
Buying a home soon? Complete our short form and we’ll connect you with the best loan options for your target property and financial situation—fast.
- Only 2 minutes to complete
- Quick turnaround on pre-approval
- No credit score impact
Got a Few Questions First?
Not Sure About Your Next Step?
Skip the guesswork. Take our quick Discovery Quiz to uncover your top financial priorities, so we can guide you toward the wealth-building strategies that fit your life.
- Takes just 5 minutes
- Tailored results based on your answers
- No credit check required
Related Posts
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get program updates and rate insights in your inbox.