No Doc Loan: 7 Strategies for Financing Without Traditional Income Documentation

Secure Mortgage Approval Using Alternative Verification Methods Beyond Standard Tax Returns and Pay Stubs
Traditional mortgage underwriting relies heavily on tax returns, pay stubs, and employment verification to assess your ability to repay. But what if your financial situation doesn’t fit these standard documentation requirements? No doc loans provide pathways to homeownership and refinancing for borrowers with complex income structures, substantial assets, privacy preferences, or non-traditional employment situations. Understanding how alternative documentation works, what lenders actually verify, and how to position yourself for approval helps you access mortgage financing that aligns with your unique financial profile rather than forcing you into conventional qualification boxes.
Key Details You’ll Learn About No Doc Loans:
- How modern no doc loans differ from pre-2008 stated income programs and why today’s alternative documentation maintains responsible lending standards
- The various no doc loan structures available including bank statement programs, asset-based qualification, DSCR investor loans, and other alternative verification methods
- Documentation that replaces traditional income verification while still demonstrating your repayment capacity to lenders (Consumer Financial Protection Bureau mortgage lending standards)
- Who benefits most from no doc loan programs including self-employed borrowers, business owners, real estate investors, retirees, and high-net-worth individuals
- Credit score, equity, and reserve requirements that typically exceed conventional loans to offset reduced income documentation
- How bank statement loans calculate qualifying income from deposit patterns instead of requiring tax returns
- Asset-based qualification mechanics that evaluate your liquid wealth rather than monthly income streams
- DSCR loan structures for investment properties that focus on rental income instead of personal income documentation
- Strategic positioning to maximize approval odds when pursuing alternative documentation financing
Ready to explore your options? Schedule a call with a loan advisor.
What Is a No Doc Loan and How Has It Evolved?
A no doc loan is a mortgage that uses alternative verification methods instead of traditional income documentation like tax returns and pay stubs. Despite the name, these programs aren’t truly “no documentation”—they simply verify your financial capacity through different means such as bank statement analysis, asset evaluation, or property cash flow rather than relying on W-2s and tax returns that many borrowers find problematic.
How do modern no doc loans differ from pre-financial crisis stated income loans? Today’s alternative documentation programs maintain responsible lending standards by verifying repayment capacity through bank deposits, asset holdings, or investment property cash flow—unlike pre-2008 stated income loans that literally took borrowers at their word without meaningful verification, creating the loan quality issues that contributed to the housing crisis.
The evolution reflects important regulatory changes. The Dodd-Frank Act and Ability-to-Repay rules established that lenders must verify a borrower’s capacity to repay mortgages. Modern no doc programs comply by using alternative verification that still demonstrates financial capacity, just through different documentation than conventional lending requires.
Common No Doc Loan Program Types
Several structures provide alternatives to traditional documentation:
- Bank statement loans – Verify income through business or personal bank account deposits over recent months instead of tax returns
- Asset-based loans – Qualify based on liquid asset holdings that could theoretically service the loan rather than monthly income
- DSCR loans – Investment property financing based on rental income coverage without personal income documentation
- 1099 income loans – Use 1099 contractor income without requiring complete business tax returns
- P&L statement programs – Accept profit and loss statements from CPAs instead of full tax return analysis
- Foreign national programs – Finance properties for non-U.S. citizens without U.S. income or credit history
- Stated asset programs – Limited programs using declared assets with verification requirements
Are no doc loans more expensive than traditional mortgages? Alternative documentation programs typically carry pricing premiums and require stronger compensating factors like larger equity contributions, higher credit scores, or substantial reserves—the reduced documentation increases lender risk, reflected in program terms.
Regulatory Compliance and Ability-to-Repay
Modern no doc programs operate within regulatory frameworks:
- Ability-to-Repay verification – Alternative methods still demonstrate capacity to manage mortgage obligations
- Qualified Mortgage standards – Most programs fall outside QM safe harbor but maintain responsible underwriting
- Non-QM lending category – Alternative documentation fits within non-qualified mortgage classification
- Portfolio lending focus – Many no doc programs come from portfolio lenders making individualized credit decisions
- Investor guidelines – Private investors purchasing these loans establish underwriting standards
The key distinction: responsible alternative documentation versus the truly no-verification stated income programs that disappeared after the financial crisis.
No Doc Loan Strategy #1: Understand Who Benefits From Alternative Documentation
Who should consider no doc loan programs? These programs serve specific borrower profiles where traditional documentation creates barriers despite strong financial capacity—self-employed individuals with tax deductions reducing reported income, business owners with complex structures, investors with property portfolios, retirees living on assets, and high-net-worth individuals prioritizing privacy.
Understanding whether your situation aligns with alternative documentation helps you pursue appropriate programs rather than struggling with conventional lending that doesn’t fit your financial profile.
Self-Employed Borrowers and Business Owners
Traditional underwriting creates challenges for entrepreneurs:
Why do self-employed borrowers struggle with conventional mortgages? Traditional lending calculates income from tax returns after accounting for business deductions—tax strategies that legitimately minimize taxable income also reduce the income lenders use for qualification, creating situations where successful business owners can’t qualify for mortgages despite strong cash flow.
Alternative documentation solves this disconnect:
- Bank statement analysis – Focuses on actual deposit patterns showing cash flow rather than tax-reduced income
- Gross revenue consideration – Some programs evaluate business revenue before deductions
- Asset-based qualification – Leverages accumulated wealth instead of focusing on reported income
- Multiple business income – Better accommodates complex income from various business entities
Self-employed scenarios benefiting from no doc programs:
- Business owners maximizing depreciation and deductions
- S-corporation owners taking distributions beyond W-2 salary
- Multiple business entities creating complex tax returns
- Newly self-employed without two-year history
- Business income trending downward on recent returns despite strong current performance
- Seasonal businesses with irregular income pattern
See how other borrowers have successfully used no-doc financing:
Calculate your no-doc loan scenarios:
- No-doc loan purchase calculator
- No-doc loan refinance calculator
- No-doc loan cash-out refinance calculator
Real Estate Investors
Investors with property portfolios face unique documentation challenges:
How do multiple properties complicate traditional mortgage qualification? Each rental property’s mortgage payment counts against your debt-to-income ratio even if properties cash flow positively—lenders may discount rental income significantly or disallow it entirely without extensive documentation, making it progressively harder to acquire additional properties through conventional financing.
No doc solutions for investors:
- DSCR loans – Qualify based on each property’s rental income covering its own debt without considering personal income
- Portfolio approaches – Evaluate entire real estate portfolio rather than individual property analysis
- Experience-based underwriting – Emphasize investment track record over personal income documentation
- Cross-collateralization – Leverage equity across multiple properties
Investor situations benefiting from alternative documentation:
- Acquiring properties beyond conventional lending limits
- Cash flow positive portfolios that appear problematic on tax returns
- Investors with properties in multiple LLCs creating complex documentation
- Foreign investors without U.S. income or credit history
- Experienced investors with strong track records but complex personal tax situations
Explore investor-focused programs:
Retirees and High-Net-Worth Individuals
Wealth doesn’t always translate to qualifying income:
Can retirees with substantial assets struggle to qualify for mortgages? Yes, traditional lending focuses on monthly income streams—retirees living on investment portfolios, drawing minimal distributions to manage taxes, or those between retirement and Social Security eligibility may have limited “qualifying income” despite substantial net worth.
Asset-based solutions address this disconnect:
- Qualification based on liquid assets that could service the mortgage
- No requirement to liquidate investments or change distribution strategies
- Recognition that substantial wealth demonstrates repayment capacity
- Accommodation of complex investment portfolios and trust structures
High-net-worth scenarios benefiting from no doc programs:
- Early retirees before Social Security or pension eligibility
- Individuals living on investment portfolios with minimal taxable distributions
- Trust beneficiaries with asset access but no traditional employment income
- Those prioritizing privacy who prefer not disclosing complete financial details
- International clients with wealth held outside U.S. requiring documentation
Explore asset-focused qualification:
How Do Bank Statement No Doc Loans Work?
What are bank statement loans and how do they verify income? Bank statement programs analyze deposit patterns in your business or personal bank accounts over recent months—typically 12 or 24 months—calculating average monthly income from consistent deposits and applying expense factors to account for business costs, resulting in qualifying income often exceeding tax return calculations.
This approach recognizes the reality that successful businesses generate cash flow shown through bank deposits regardless of how tax returns report income after deductions optimize tax liability.
Bank Statement Income Calculation
Lenders follow systematic processes to derive qualifying income:
- Statement collection – Gather 12 or 24 months of bank statements showing all deposits
- Deposit analysis – Review all deposits entering the accounts during the period
- Transfer exclusion – Remove transfers between accounts, duplicate deposits, or one-time events
- Average monthly calculation – Calculate average monthly deposits over the analysis period
- Expense factor application – Apply percentage (commonly 25-50%) representing business expenses
- Qualifying income determination – Resulting figure becomes your qualifying monthly income
Why do bank statement loans apply expense factors? Your bank deposits include gross business revenue, but running your business costs money—the expense factor (25-50% depending on business type and program) accounts for business expenses you must pay from gross deposits, leaving the net amount available for personal obligations like your mortgage.
Personal vs. Business Bank Statements
Programs accept different statement types:
Business bank statements:
- Show actual business revenue and deposit patterns
- Typically use 50% expense factor (allowing 50% of deposits as qualifying income)
- Best for borrowers with clean business banking separating personal and business finances
- Requires business license or documentation proving business operation
Personal bank statements:
- Show deposits from various sources including business income mixed with personal funds
- Typically use 25% expense factor (allowing 75% of deposits as qualifying income)
- Works for those without separate business banking
- May include personal deposits like gifts or transfers requiring explanation
Mixed statement approach:
- Some programs allow analyzing both business and personal accounts
- Useful when income flows through multiple accounts
- Requires careful tracking to avoid double-counting deposits
Documentation Requirements
Bank statement loans require specific documentation beyond the statements:
- Bank statements for chosen period (12 or 24 months) from all accounts
- Business license or documentation proving legitimate business operation
- CPA letter supporting business operation and income (sometimes required)
- Credit report authorization
- Asset statements showing reserves
- Property documentation for purchase or refinance
- Explanation letters for any unusual deposits or patterns
What deposits require explanation in bank statement analysis? Large one-time deposits, transfers between accounts, gifts, loan proceeds, or any irregular deposits not representing business income need documented explanations—lenders want to verify qualifying income comes from sustainable business operations rather than one-time events.
What Are the Credit and Financial Requirements for No Doc Loans?
What credit score do you need for no doc loan approval? Alternative documentation programs typically require higher credit scores than conventional mortgages—many programs establish minimums in the excellent range to offset the reduced income verification, though specific thresholds vary by lender, loan amount, and compensating factors like equity and reserves.
The reduced documentation increases lender risk, requiring compensating factors through other underwriting elements to maintain responsible lending standards.
Credit Profile Standards
No doc programs demand strong credit positioning:
- Higher minimum scores – Requirements typically exceed conventional loan minimums by significant margins
- Clean payment history – Recent late payments, especially on mortgages or installment debt, create challenges
- Low credit utilization – Revolving debt well below available credit limits demonstrates financial discipline
- Established credit depth – Long credit history with diverse account types
- Limited recent inquiries – Minimal new credit applications before your mortgage application
- Clean public records – No recent bankruptcies, foreclosures, judgments, or significant collections
How do recent credit issues affect no doc loan approval? Alternative documentation programs offer less flexibility for recent credit problems than conventional loans since they’re already accommodating reduced income verification—combining both alternative documentation and challenged credit typically exceeds most lenders’ risk tolerance.
Equity and Down Payment Requirements
Larger equity contributions offset documentation reduction:
Typical equity requirements:
- Primary residence purchases often require substantially higher contributions than conventional loans
- Investment properties and second homes require even larger equity positions
- Cash-out refinances may have stricter loan-to-value limits than purchase transactions
- Properties in certain locations or of unique types may require additional equity
Why do no doc loans require more equity? Larger borrower investment reduces lender risk exposure—if market conditions decline, greater equity cushion protects against loss, while substantial borrower investment also demonstrates financial commitment and capacity.
Benefits of larger equity contributions:
- Improved approval odds when documentation is limited
- Better pricing tiers as equity increases
- Reduced monthly payment obligations
- Greater negotiating flexibility with underwriters
- Protection against market value fluctuations
Reserve Requirements
Substantial liquid reserves are critical for no doc approval:
Minimum reserve expectations:
- Many programs require 6-12+ months of total housing payments in liquid reserves after closing
- Investment properties may require reserves for both subject property and primary residence
- Multiple financed properties require reserves covering all properties
- Reserve requirements increase with risk factors like lower credit scores or higher loan amounts
What assets count toward no doc loan reserves? Checking accounts, savings accounts, money market funds, stocks, bonds, mutual funds in liquid brokerage accounts, and sometimes retirement accounts (potentially discounted) count toward reserves—illiquid assets like real estate equity, business interests, or collectibles typically don’t qualify.
Reserve calculation example:
- If your total housing payment (principal, interest, taxes, insurance) will be $5,000 monthly
- 12 months of reserves requires $60,000 in liquid assets
- This must remain after your down payment and closing costs
- Multiple properties multiply this requirement
No Doc Loan Strategy #2: Leverage Asset-Based Qualification
How do asset-based no doc loans work? These programs qualify you based on liquid asset holdings rather than requiring income documentation—lenders evaluate whether your assets could theoretically service the mortgage over specific timeframes, creating qualification pathways for those with substantial wealth but limited traditional income.
Asset-based lending recognizes that significant liquid wealth demonstrates financial capacity regardless of monthly income streams shown on tax returns or pay stubs.
Asset-Based Calculation Methods
Lenders use various formulas to derive qualifying capacity from assets:
Asset depletion method:
- Divides your total liquid assets by specific number of months (commonly 84-360)
- Resulting monthly figure represents your “income” for qualification purposes
- Example: $2,000,000 in assets ÷ 240 months = $8,333 monthly qualifying income
- Longer depletion periods create higher qualifying income figures
Debt service coverage:
- Evaluates whether assets could cover mortgage payments over loan term
- May require assets covering 2-5+ years of payments depending on program
- Focuses on payment coverage rather than deriving monthly income figure
Percentage of assets:
- Some programs simply require assets exceeding specific multiples of loan amount
- Example: Liquid assets totaling 2-3x the requested loan amount
- Simplest calculation but typically requires substantial asset positions
How much in assets do you need for asset-based qualification? Requirements vary significantly by program and loan amount, but many asset-based programs require liquid assets substantially exceeding the loan amount—ratios of 2-4x the loan amount in qualifying assets occur commonly.
Qualifying Asset Types
Not all assets receive equal treatment:
Full value assets:
- Cash in checking and savings accounts
- Money market funds
- Certificates of deposit
- Stocks and bonds in liquid brokerage accounts
- Mutual funds in accessible accounts
Discounted assets (commonly 60-70% of value):
- Retirement accounts (401k, IRA, etc.) subject to withdrawal penalties
- Cash value life insurance policies
Typically excluded assets:
- Real estate equity
- Business ownership interests
- Collectibles, art, jewelry
- Cryptocurrency (most lenders currently)
- Retirement accounts with significant withdrawal restrictions
- Assets in foreign accounts without clear accessibility
Asset-Based Program Documentation
While eliminating income documentation, asset-based programs require comprehensive asset verification:
- Complete statements for all asset accounts (typically 2-3 months)
- Documentation of account ownership and accessibility
- Asset transfer history showing seasoning requirements met
- Letters from financial institutions confirming account access
- Trust documents if assets held in trust structures
- Explanation of any unusual asset movements or large withdrawals
- Credit report authorization
- Property documentation for purchase or refinance
Do asset-based loans require explanation of wealth source? Many programs want to understand how you accumulated assets, particularly with very large holdings—this isn’t to judge but to verify assets come from legitimate sources and truly belong to you rather than being temporarily borrowed for qualification purposes.
Explore asset-based qualification:
Strategy #3: Use DSCR Loans for Investment Property No Doc Financing
What are DSCR no doc loans and how do they work? Debt Service Coverage Ratio loans for investment properties qualify you based on the property’s rental income covering its mortgage payment—your personal income doesn’t factor into qualification, making DSCR loans effectively “no doc” for personal income while focusing entirely on investment property cash flow.
This structure recognizes that well-selected investment properties should be self-sustaining regardless of the owner’s personal income situation.
DSCR Calculation Mechanics
The debt service coverage ratio measures whether rental income covers the mortgage:
DSCR formula: DSCR = Monthly Rental Income ÷ Monthly Mortgage Payment (PITI)
DSCR interpretation:
- DSCR of 1.0 = Rental income exactly equals mortgage payment
- DSCR above 1.0 = Rental income exceeds mortgage payment (positive cash flow)
- DSCR below 1.0 = Rental income doesn’t cover payment (negative cash flow)
Minimum DSCR requirements:
- Most programs require DSCR of 1.0 or higher for approval
- Some lenders accept DSCR slightly below 1.0 (0.75-0.99) with compensating factors
- Higher DSCR ratios improve approval odds and may affect pricing
- DSCR requirements vary by lender and overall risk profile
How do lenders determine rental income for DSCR calculations? Most commonly through market rent appraisals where the property appraiser researches comparable rental properties and provides opinion of reasonable market rent for your property—alternatively, existing leases on occupied properties provide actual rental income verification.
DSCR Loan Advantages for Investors
Investment property financing without personal income documentation:
- No personal income verification – Your tax returns, pay stubs, and employment don’t matter
- Unlimited property accumulation – Each property qualifies on its own merits without debt-to-income ratio constraints
- Self-employment friendly – Business structure and income complexity irrelevant to qualification
- Portfolio growth enabler – Acquire multiple properties without personal debt ratio limitations
- Foreign national access – Non-U.S. citizens can invest in U.S. real estate without domestic income
- Privacy preservation – No need to disclose complete personal financial details
Can you use DSCR loans for your first investment property? Yes, DSCR programs don’t typically require previous investment property experience, though lenders may adjust terms or requirements for first-time investors—the focus remains on whether the specific property’s income covers its debt service.
DSCR Loan Documentation Requirements
While eliminating personal income documentation, DSCR loans require property-specific verification:
- Property appraisal with market rent analysis
- Existing lease agreements if property is currently rented
- Property insurance quote
- Property tax documentation
- HOA documents if applicable
- Credit report (personal credit still matters for approval)
- Asset statements showing required reserves
- Down payment source documentation
Explore DSCR investment property financing:
- DSCR Loan
- View DSCR loan case studies
- View DSCR refinance case studies
- View DSCR cash-out refinance case studies
Calculate DSCR scenarios:
What Property Types and Loan Purposes Work With No Doc Loans?
Can you use no doc loans for any property type? Most alternative documentation programs finance a wide range of property types including single-family homes, condos, townhomes, and 2-4 unit properties, though specific programs have preferences—DSCR loans focus on investment properties while bank statement and asset-based programs typically serve primary residences, second homes, and investment properties.
Understanding program-specific property and purpose preferences helps you pursue appropriate financing for your situation.
Property Type Considerations
Different programs accommodate various property types:
Primary residences:
- Bank statement loans work well for self-employed primary residence purchases
- Asset-based qualification available for primary homes
- Generally offer most favorable terms within no doc lending
- Widest range of alternative documentation options
Second homes:
- Available through most no doc programs
- Typically require larger equity contributions than primary residences
- Reserve requirements cover both properties
- May have slightly different pricing than primary homes
Investment properties:
- DSCR loans specifically designed for rental properties
- Bank statement and asset-based programs also available for investments
- Higher equity requirements than primary residences
- Focus on property fundamentals and rental income potential
Multi-unit properties (2-4 units):
- Available through specialized no doc programs
- DSCR calculation can include all rental units
- Owner-occupied multi-units may qualify for better terms
- Complex income from multiple units works well with alternative documentation
Condos and townhomes:
- Most programs finance condos with proper project approval
- May require higher equity or have pricing adjustments
- Project financial health and owner-occupancy ratios matter
- Warrantable vs. non-warrantable condo classification affects availability
Can you use no doc loans for unique or luxury properties? Yes, alternative documentation programs often work well for high-value or unique properties that might challenge conventional lending—portfolio lenders providing no doc options frequently have experience with luxury real estate and can accommodate properties exceeding conforming loan limits.
Loan Purpose Flexibility
No doc programs serve various financing needs:
Purchase transactions:
- Buy primary residences without traditional income documentation
- Acquire investment properties based on their cash flow
- Purchase second homes or vacation properties
- Finance properties that conventional lenders might decline
Rate-and-term refinances:
- Lower your interest rate without income documentation
- Modify loan structure or term without tax return requirements
- Consolidate first and second liens
- Remove co-borrowers or add borrowers to title
Cash-out refinances:
- Extract equity for various purposes without income verification
- Fund business investments using home equity
- Consolidate debt through home equity access
- Access capital for additional real estate investments
How much equity can you extract with no doc cash-out refinancing? Cash-out refinance loan-to-value limits vary by program but typically range more conservatively than conventional lending—expect maximum LTV ratios that require you to maintain substantial equity positions after extracting cash.
Considering a refinance? Submit a refinance inquiry to see if this makes sense for you.
No Doc Loan Strategy #4: Optimize Your Application for Alternative Documentation
How can you maximize approval odds for no doc loans? Strong positioning through excellent credit management, substantial equity contributions, significant reserve accumulation, clear bank deposit patterns, and professional documentation presentation dramatically improve approval likelihood—alternative documentation doesn’t mean relaxed standards, but rather different evaluation criteria requiring strategic preparation.
Thoughtful application preparation demonstrates financial sophistication and repayment capacity even without traditional income documentation.
Credit Profile Optimization
Perfect your credit before applying:
- Review all three bureau reports – Check for errors and dispute inaccuracies well in advance
- Pay down revolving balances – Get credit card balances to very low percentages of limits
- Maintain perfect payment history – Ensure no late payments in months preceding application
- Avoid new credit – Don’t open accounts or make major credit purchases before applying
- Keep old accounts open – Maintain credit history length by not closing old accounts
- Become authorized user – If you have thin credit, authorized user status on established accounts helps
- Address collections strategically – Consult credit professionals about handling old collections
How far in advance should you optimize credit for no doc loan application? Begin credit optimization 6-12 months before your anticipated application—this timeframe allows late payments to age off consideration, gives you time to pay down balances, lets you dispute errors thoroughly, and permits your credit profile to stabilize after any improvements.
Bank Statement Preparation
If pursuing bank statement loans, prepare your accounts strategically:
- Separate business and personal finances – Clean banking makes analysis easier and more favorable
- Maintain consistent deposit patterns – Irregular or sporadic deposits create qualification challenges
- Document unusual deposits – Prepare explanations for any large one-time deposits or transfers
- Avoid excessive transfers – Moving money between accounts creates confusion in analysis
- Use business accounts – If you have business banking, use it consistently for business deposits
- Build deposit history – Most programs require 12-24 months of statements, so plan accordingly
Can you improve bank statement loan qualification by changing deposit patterns? While you shouldn’t artificially manipulate finances, legitimately depositing all business revenue through proper business accounts and maintaining consistent patterns does improve how lenders analyze your income—start these practices well before applying rather than making sudden changes right before application.
Reserve Accumulation
Build substantial liquid reserves:
- Start saving early – Accumulate reserves well before your application
- Liquidate non-liquid assets if needed – Convert business ownership or real estate to liquid assets
- Document asset seasoning – Most programs require assets seasoned for 2-3 months
- Consolidate accounts – Fewer accounts with larger balances are easier to document
- Maintain clear ownership – Assets must be in your name or properly documented if in trusts
- Avoid large withdrawals – Don’t deplete reserves before or during application process
How much should you have in reserves for no doc loan approval? Target 12-24 months of total housing payments in liquid reserves after your down payment and closing costs—this substantial cushion demonstrates financial capacity and addresses lender concerns about reduced income documentation.
Professional Documentation Presentation
Organize your application professionally:
- Create cover letter explaining your situation and why alternative documentation fits
- Organize documents logically with clear labels and sections
- Provide explanation letters for anything unusual or complex
- Include CPA letters supporting your business and income if applicable
- Present complete documentation rather than forcing lenders to request additional items
- Demonstrate financial sophistication through clear, professional presentation
Professional presentation signals that you’re serious, organized, and financially sophisticated—these impressions matter significantly when underwriters evaluate applications with alternative documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions About No Doc Loans
Are No Doc Loans Legal and Safe?
Are no doc loans legal in today’s mortgage market? Yes, alternative documentation programs operate legally within current regulatory frameworks by verifying repayment capacity through alternative means that comply with Ability-to-Repay requirements—modern no doc loans maintain responsible lending standards while accommodating borrowers whose income doesn’t fit traditional documentation methods.
The key distinction from problematic pre-crisis lending:
- Modern programs verify financial capacity through alternative documentation
- Lenders maintain underwriting standards with compensating factors
- Programs operate within regulatory compliance frameworks
- Borrowers must still demonstrate ability to repay through some verification method
- No longer allow pure “stated income” without any verification
Are no doc loans safe for borrowers? Yes, when pursued appropriately for situations where they fit—borrowers should ensure they can truly afford the mortgage payment based on their actual financial situation regardless of what documentation shows, maintain adequate reserves for emergencies, understand the terms and costs, and work with reputable lenders following responsible underwriting practices.
Can You Refinance a No Doc Loan Later?
Yes, no doc loans can be refinanced through conventional or other alternative documentation programs when circumstances change or market conditions create opportunities—the existing no doc loan doesn’t prevent future refinancing, though you’ll need to qualify under whatever program you choose for the refinance based on requirements at that time.
Should you plan to refinance your no doc loan to conventional financing later? This strategy works well if you anticipate your documentation situation improving—for example, self-employed borrowers might take no doc loans initially then refinance to conventional terms after establishing two years of tax returns showing adequate income, or retirees might refinance once Social Security creates qualifying income streams.
Refinance planning considerations:
- Monitor market conditions for favorable refinancing opportunities
- Work on credit profile improvements in the meantime
- Build additional equity through payments or value appreciation
- Develop documentation that would support conventional refinancing
- Maintain good payment history on your no doc loan
- Accumulate reserves exceeding typical requirements
How Quickly Can You Close a No Doc Loan?
No doc loan timelines vary based on loan complexity and documentation completeness, but typically align with or slightly exceed conventional mortgage timelines—expect 30-45 days for straightforward transactions, though complex situations or unique properties may require longer, while well-prepared applications with complete documentation can sometimes close faster.
What factors affect no doc loan closing speed?
- Documentation completeness at application
- Bank statement analysis complexity if using that program
- Asset verification requirements and account documentation
- Property appraisal scheduling and completion
- Lender underwriter workload and experience with alternative documentation
- Title work complexity
- Your responsiveness to any additional documentation requests
Expedite your closing:
- Gather all documentation before applying
- Work with lenders experienced in alternative documentation
- Respond immediately to any underwriter requests
- Schedule appraisal promptly
- Maintain clear communication throughout process
- Avoid making financial changes during processing
Can Foreign Nationals Get No Doc Loans?
Yes, foreign national programs provide no doc financing for non-U.S. citizens purchasing U.S. real estate without requiring U.S. income, credit history, or employment—these programs focus on property equity, foreign income and assets, and the property itself as collateral, making them effectively alternative documentation for international buyers.
What do foreign nationals need for no doc loan approval? Valid passport and visa documentation, foreign income verification (often simplified compared to U.S. requirements), foreign bank statements showing financial capacity, substantial equity contributions (typically larger than U.S. citizen requirements), U.S. tax identification number (ITIN), proof of funds for down payment, and sometimes U.S. bank account establishment.
Foreign national considerations:
- Larger equity requirements than U.S. citizen programs
- Properties typically in established markets or major metro areas
- Focus on property fundamentals and borrower equity investment
- May require U.S.-based bank accounts for payments
- Tax withholding and reporting requirements differ from U.S. citizens
- Estate planning considerations for foreign-owned U.S. property
Do All Lenders Offer No Doc Loans?
No, alternative documentation programs come primarily from portfolio lenders, non-QM specialists, and private lenders rather than being widely available across all mortgage lenders—many large retail mortgage companies focus exclusively on conforming loans that can be sold to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, while smaller portfolio lenders and specialty lenders provide most no doc programs.
How do you find lenders offering no doc loans? Work with mortgage brokers who have access to multiple no doc lenders, research portfolio lenders in your market that hold loans on their balance sheets, explore non-QM lending specialists, connect with lenders serving self-employed borrowers or real estate investors, and ask for referrals from real estate attorneys, CPAs, or other investors.
Types of lenders offering no doc programs:
- Portfolio banks holding loans on their balance sheets
- Non-QM lenders specializing in alternative documentation
- Private lenders and hard money sources (typically short-term)
- Credit unions with portfolio lending programs
- Specialized mortgage companies focused on self-employed or investor borrowers
Strategy #5: Compare No Doc Loan Costs and Terms Carefully
Are no doc loan costs significantly higher than conventional mortgages? Alternative documentation programs typically carry pricing premiums through higher interest rates, additional fees, or both—the reduced documentation increases lender risk, reflected in program costs, though exact pricing varies significantly based on your overall risk profile, equity contribution, credit score, and chosen program.
Understanding total costs across different no doc programs helps you select the most cost-effective option for your situation while weighing benefits against expenses.
Interest Rate Expectations
No doc programs generally carry rate premiums:
- Pricing typically exceeds conventional mortgage rates by varying margins
- Your credit score, equity, and reserves significantly affect your specific rate
- Different alternative documentation programs have different rate structures
- Market conditions influence the spread between conventional and no doc rates
- Portfolio lender relationships may provide pricing advantages
What factors most affect your no doc loan interest rate? Credit score stands as the primary driver within most programs, with larger equity contributions, substantial reserves, strong bank deposit patterns, and program selection all materially impacting pricing—improving these factors before applying can shift you into better pricing tiers.
Fee Structures
Alternative documentation may involve additional costs:
- Origination fees – Some programs charge higher origination fees than conventional loans
- Underwriting fees – Additional underwriting analysis may carry premium charges
- Document review fees – Bank statement analysis or asset verification may involve fees
- Appraisal costs – Generally similar to conventional loans
- Third-party fees – Title, escrow, and recording fees align with traditional mortgages
Are no doc loan closing costs substantially higher? Total closing costs depend on specific lender fee structures—while some no doc lenders charge premium fees, others maintain fee structures competitive with conventional lending, making lender comparison important for understanding total transaction costs.
Total Cost Analysis
Evaluate the complete cost picture:
- Calculate total interest over expected holding period – Not just the rate but total interest paid
- Include all upfront fees and costs – Origination, underwriting, and other charges
- Consider opportunity cost – What would you earn if you made larger down payment?
- Factor in refinancing potential – Might you refinance to conventional terms later?
- Weigh against alternatives – Compare to waiting and qualifying conventionally
- Evaluate time value – Is purchasing now worth the premium versus waiting?
When do no doc loan costs justify the expense? If alternative documentation enables purchasing a property that will appreciate significantly, accessing your current home’s equity for high-return investments, avoiding liquidation of well-performing assets, maintaining business operations without disruption, or acquiring cash-flowing investment properties that self-fund the premium costs through rental income.
No Doc Loan Strategy #6: Understand State and Property Restrictions
Do all states allow no doc loans? While most states permit alternative documentation lending, specific program availability varies by state based on state-specific lending regulations, lender licensing, investor guidelines for purchasing these loans, and local market conditions—some states have more restrictive consumer protection laws affecting non-QM lending availability.
Additionally, certain property types or locations may face availability limitations regardless of state regulations.
State-Specific Considerations
Alternative documentation availability varies geographically:
- Licensing requirements – Lenders must be licensed in your state to offer programs there
- State regulations – Some states have additional consumer protection laws affecting non-QM lending
- Investor appetite – Private investors purchasing no doc loans may have state preferences
- Market conditions – Strong real estate markets typically have better program availability
- Lender concentration – States with more portfolio lenders offer more alternative documentation options
What states have the best no doc loan availability? Generally states with strong real estate markets, significant self-employment populations, large investor communities, and active portfolio lending institutions—major markets in California, Florida, Texas, New York, and other populous states typically offer robust alternative documentation options.
Property Location Factors
Not all property locations receive equal treatment:
Preferred locations:
- Established urban and suburban markets with stable property values
- Areas with strong comparable sales data for appraisal purposes
- Markets with active real estate investment communities
- Locations where lenders have experience and comfort
Challenging locations:
- Very rural properties with limited comparable sales
- Markets with declining property values or economic challenges
- Areas with very high or very low property values creating limited comparables
- Locations with unique property types dominating the market
- Regions experiencing significant natural disaster risk
Can you get no doc loans for rural properties? Yes, though availability narrows and requirements may strengthen—rural property no doc financing typically requires larger equity contributions, may involve specialized lenders with rural expertise, could carry different pricing, and benefits from properties with income-generating potential like farms or ranches.
Strategy #7: Work With Experienced No Doc Loan Specialists
Why does lender selection matter more for no doc loans than conventional mortgages? Alternative documentation requires specialized expertise, different underwriting approaches, portfolio lending relationships, and experience navigating complex financial situations—working with lenders inexperienced in no doc programs leads to declined applications, unnecessary documentation requests, extended timelines, and potentially missing optimal programs for your situation.
Specialist lenders understand how to present and underwrite alternative documentation effectively.
Identifying Qualified Lenders
Look for specific experience indicators:
- Portfolio lending focus – Lenders holding loans rather than selling them to Fannie/Freddie
- Non-QM specialization – Companies specifically focused on alternative documentation
- Self-employed expertise – Track record serving business owners and entrepreneurs
- Investor experience – History with real estate investor financing
- Multiple program access – Relationships with various no doc program investors
- Clear program explanations – Ability to articulate how different programs work
- Professional references – CPA, attorney, or other professional referrals
How do mortgage brokers help with no doc loans? Experienced brokers maintain relationships with multiple no doc lenders and programs, can match your situation to optimal programs, understand various lender overlays and preferences, navigate complex underwriting requirements, and advocate on your behalf when issues arise—their multi-lender access proves particularly valuable in specialized lending.
Questions to Ask Potential Lenders
Evaluate lenders through targeted questions:
- What percentage of your business involves alternative documentation?
- Which specific no doc programs do you offer?
- What’s your experience with situations like mine?
- Can you provide references from similar borrowers?
- What’s your typical timeline for no doc loans?
- How do you handle underwriting for complex situations?
- What’s your approval rate for alternative documentation?
- Can you explain your pricing structure clearly?
Lenders with genuine expertise provide clear, confident answers demonstrating deep program knowledge.
Red Flags to Avoid
Watch for concerning lender behaviors:
- Promising approval without reviewing your actual financial situation
- Unable to explain clearly how programs calculate qualifying income
- Offering terms that seem too good to be true compared to market
- Requesting large upfront fees before substantive work begins
- Lacking proper licensing or credentials
- Unable to provide professional references
- Pushing you toward programs that don’t align with your needs
- Poor communication or responsiveness during initial discussions
Should you get multiple no doc loan quotes? Yes, comparing terms across lenders reveals market pricing and helps identify optimal programs—however, timing applications strategically to minimize credit inquiries and working with experienced lenders who can pre-qualify you before formal applications prevents application denials affecting your credit profile.
Alternative Loan Programs to Consider
If a no-doc loan isn’t the right fit, consider these alternatives:
- Asset-Based Loan – Leverage investment portfolios and liquid assets with minimal income verification
- Bank Statement Loan – For self-employed borrowers using 12-24 months of bank deposits for qualification
- Profit and Loss Loan – Qualify using CPA-prepared financial statements instead of tax returns
- DSCR Loan – For investment properties qualifying based on rental cash flow without personal income documentation
- Foreign National Loan – For non-U.S. citizens with limited U.S. documentation
Explore all 30+ loan programs to find your best option.
Not sure which program is right for you? Take our discovery quiz to find your path.
Helpful No Doc Loan Resources
Official Government Guidance
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau Ability-to-Repay Rule – Federal consumer protection agency explaining mortgage lending standards including Ability-to-Repay requirements that govern responsible alternative documentation lending practices.
Federal Trade Commission Mortgage Discrimination Information – FTC resource covering fair lending laws, discrimination protections, and borrower rights that apply equally to alternative documentation and conventional mortgage programs.
Industry Organizations
Mortgage Bankers Association Non-QM Lending Resources – National trade association providing research, market data, and industry perspective on non-qualified mortgage lending including alternative documentation programs and market trends.
National Association of Realtors Investment Property Resources – Real estate professional organization offering investment property data, market analysis, and resources relevant to investors using alternative documentation for property acquisition.
Educational Resources
IRS Small Business and Self-Employed Tax Center – Official IRS resource for self-employed individuals explaining tax filing, business deductions, and income reporting that affects traditional mortgage qualification and drives need for alternative documentation.
U.S. Small Business Administration Business Resources – Federal agency supporting small businesses with educational resources, business planning tools, and financial management guidance helpful for self-employed borrowers navigating alternative documentation requirements.
Federal Reserve Consumer Credit and Mortgage Resources – Central bank educational materials explaining mortgage markets, interest rate factors, and economic conditions influencing both conventional and alternative documentation lending availability and pricing.
Need local expertise? Get introduced to trusted partners including loan officers, realtors, and contractors in your area.
Ready to get started? Apply now or schedule a call to discuss your situation.
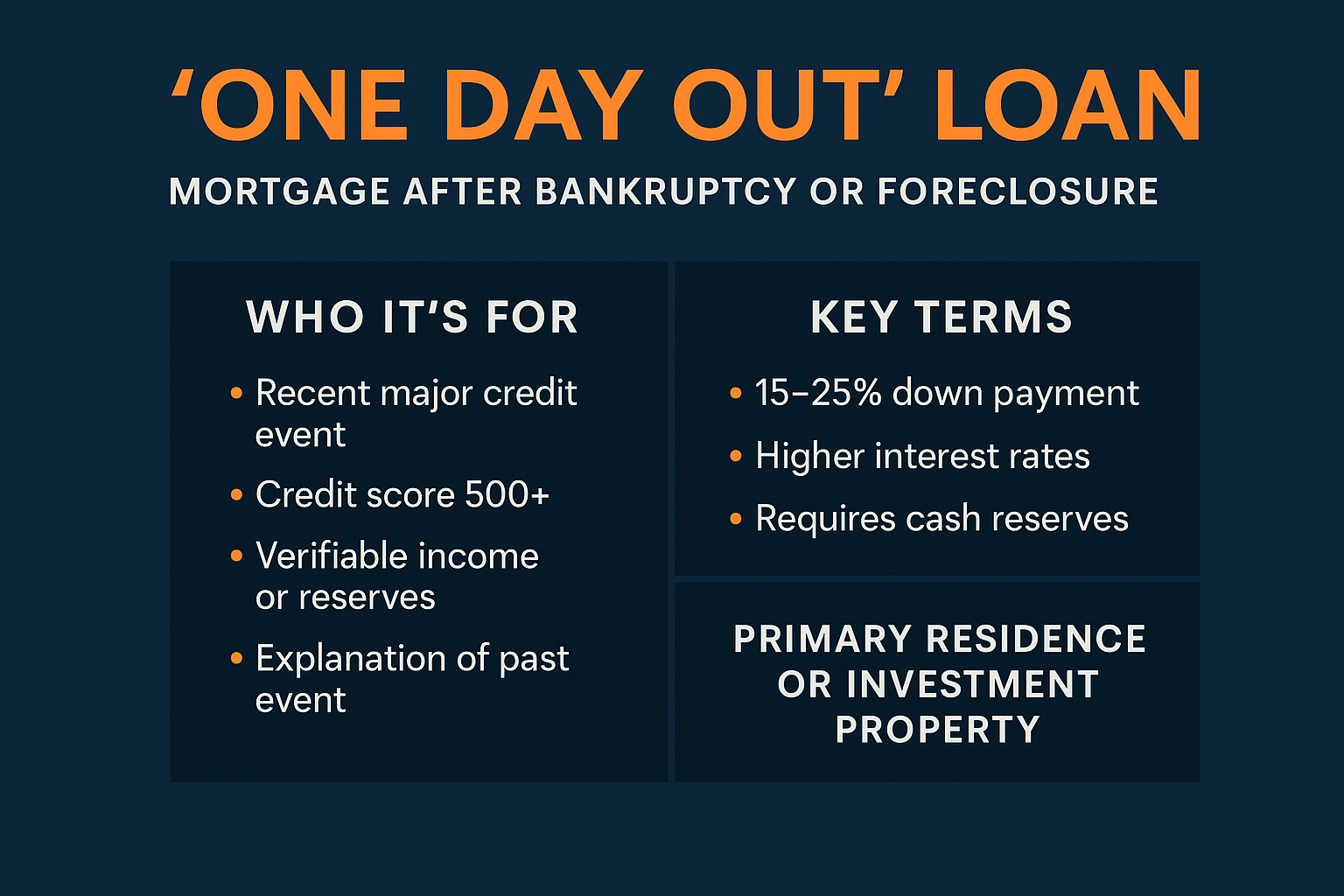
What You Need to Know
These loans come with stricter terms:
- Down payments are typically 15–25%
- Interest rates are higher than conventional loans
- Some lenders require six months to two years of reserves
But the benefits are clear: you can stop renting, re-enter the market, and rebuild wealth while others are still waiting for their credit to recover.
Strategy: Refinance Later
Many buyers use this loan to purchase now, then refinance into a lower-rate, full-doc mortgage once they’ve met the conventional waiting periods and improved their credit.
This creates a bridge back into homeownership—without losing years to rent.
Let’s Talk About Your Situation
You’re not alone, and you’re not disqualified. We help buyers every day who’ve gone through what you have.
Let’s figure out what you qualify for and build a path forward.
Need a Pre-Approval Letter—Fast?
Buying a home soon? Complete our short form and we’ll connect you with the best loan options for your target property and financial situation—fast.
- Only 2 minutes to complete
- Quick turnaround on pre-approval
- No credit score impact
Got a Few Questions First?
Not Sure About Your Next Step?
Skip the guesswork. Take our quick Discovery Quiz to uncover your top financial priorities, so we can guide you toward the wealth-building strategies that fit your life.
- Takes just 5 minutes
- Tailored results based on your answers
- No credit check required
Related Posts
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get program updates and rate insights in your inbox.