Manufactured Home Financing Options: 7 Ways to Secure Affordable Housing with Government-Backed Loans

Key Details: What You’ll Learn About Manufactured Home Financing
- Manufactured home financing includes FHA loans, VA loans, USDA loans, and conventional mortgages when homes meet specific construction and installation standards (HUD manufactured housing standards)
- Manufactured homes built after June 15, 1976 must comply with HUD Code requirements including permanent foundation installation for real property financing (HUD permanent foundation requirements)
- Government-backed programs offer attractive down payment options—as low as zero down with VA financing or minimal down payment with FHA programs (VA manufactured home loan requirements)
- Manufactured homes in land-lease communities, on owned land, or with purchased lots qualify under different program requirements with varying terms and conditions
- Chattel loans finance manufactured homes as personal property when permanent foundation attachment isn’t feasible, though terms differ from real property mortgages (CFPB chattel loan information)
- Refinancing options include cash-out refinancing, rate-and-term refinancing, and home equity access when homes meet lender standards
- Title status matters significantly—homes titled as real property typically qualify for conventional mortgage programs while personal property titles may require specialized chattel financing (Fannie Mae manufactured housing guidelines)
Ready to explore your options? Schedule a call with a loan advisor.
Understanding Manufactured Home Financing Fundamentals
Manufactured home financing has evolved dramatically over recent decades, transforming from limited chattel loan options to comprehensive mortgage programs rivaling traditional home financing. Today’s manufactured housing market offers legitimate pathways to homeownership through government-backed programs, conventional mortgages, and specialized lending solutions.
The key distinction lies in understanding how manufactured homes differ from traditional site-built construction. Manufactured homes are built entirely in controlled factory environments according to HUD Code standards, then transported to permanent or semi-permanent locations. This construction method creates quality, affordable housing options increasingly popular across the United States.
Modern FHA financing, VA benefits, and USDA rural housing programs now accommodate manufactured homes meeting specific criteria. These programs recognize manufactured housing as viable, quality construction deserving the same financing support as traditional homes. Understanding which programs work for your situation creates pathways to affordable homeownership.
This comprehensive guide explores every major manufactured home financing option, qualification requirements, foundation standards, title conversion processes, and strategic approaches maximizing your borrowing power. Whether you’re purchasing your first home, upgrading from a rental, or investing in affordable housing, we’ll show you how to navigate manufactured home financing successfully.
FHA Manufactured Home Loans: Government-Backed Affordability
Title I vs Title II FHA Programs
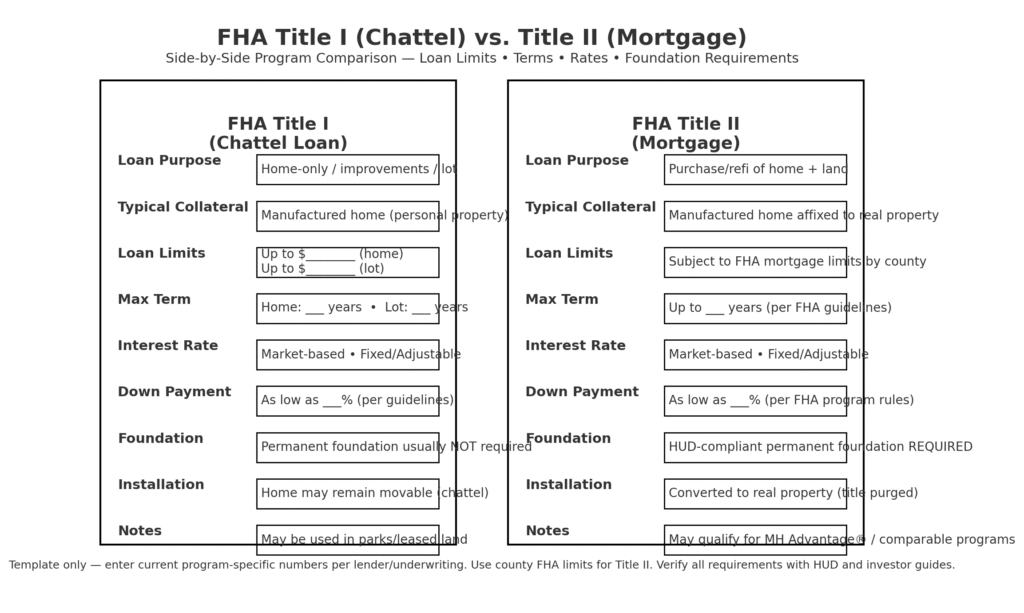
FHA manufactured home financing operates through two distinct programs serving different needs. Title I loans finance manufactured homes as personal property with smaller loan limits and shorter terms, while Title II programs provide traditional mortgage financing when homes qualify as real property attached to permanent foundations.
Title II financing offers superior terms—competitive interest rates comparable to site-built home mortgages, longer repayment periods extending twenty to thirty years, and substantial loan limits supporting quality housing purchases. These mortgages function identically to traditional FHA loans for site-built properties when manufactured homes meet specific standards.
The critical determining factor separates personal property from real property status. Homes permanently affixed to land through proper foundation systems and converted to real property titles qualify for Title II financing. This conversion process, though requiring careful attention to detail, opens doors to dramatically better financing terms supporting long-term homeownership.
Use the FHA loan calculator to model potential payments under different scenarios. See how other borrowers successfully navigated FHA financing in our case studies demonstrating practical application of these programs.
Permanent Foundation Requirements
Permanent foundation installation represents the cornerstone requirement for traditional mortgage financing on manufactured homes. HUD establishes specific standards defining acceptable permanent foundation systems ensuring structural integrity, weather protection, and long-term stability matching site-built home construction.
Acceptable permanent foundation systems include full perimeter concrete or masonry foundations, concrete slab foundations, reinforced piers and beam systems meeting engineering standards, and basement foundations comparable to traditional construction. The foundation must support the entire home structure, resist settling and movement, and protect against moisture infiltration and pest damage.
Professional engineering certifications typically accompany permanent foundation installations, documenting compliance with HUD standards and local building codes. These certifications become crucial during the financing process, providing lenders assurance that properties meet long-term stability requirements supporting mortgage investments.
Many manufactured home communities now install permanent foundations as standard practice, recognizing how this enhancement expands financing options for buyers. If you’re purchasing a home requiring foundation work, specialized renovation financing can sometimes bundle purchase and foundation costs into single loan packages.
Down Payment and Credit Requirements
FHA manufactured home loans offer accessible down payment requirements making homeownership realistic for first-time buyers and families with modest savings. Minimum down payments typically start around the same levels as traditional FHA financing, though specific requirements vary based on credit profiles and property characteristics.
Credit score requirements for manufactured home financing generally mirror traditional FHA standards, with flexibility for borrowers rebuilding credit or establishing credit history. The program recognizes manufactured housing as legitimate, quality construction deserving the same underwriting consideration as site-built homes.
Debt-to-income ratio standards apply similarly to traditional financing, evaluating your ability to comfortably manage mortgage payments alongside existing financial obligations. Use the FHA calculator to explore how different down payment amounts affect your monthly obligations and qualification ratios.
Documentation requirements focus on verifying income stability, employment continuity, and financial reserves supporting homeownership success. The process closely parallels traditional mortgage qualification, though lenders may request additional documentation confirming permanent foundation installation and proper title conversion when applicable.
VA Loans for Manufactured Homes: Military Benefits and Zero Down Payment
VA Manufactured Home Eligibility
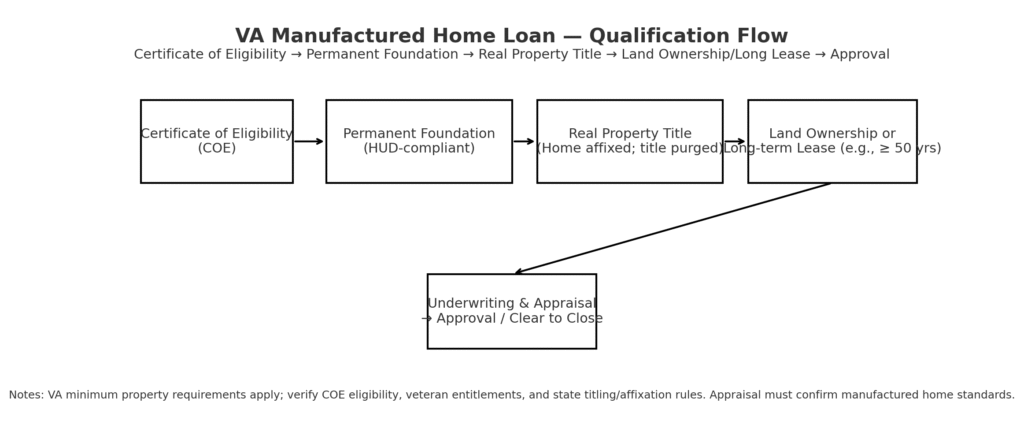
VA loan benefits extend to manufactured homes when veterans, active duty service members, and eligible surviving spouses meet program requirements and properties satisfy specific standards. This powerful benefit eliminates down payment requirements, removes private mortgage insurance obligations, and provides competitive interest rates supporting affordable homeownership.
Manufactured homes financed through VA programs must meet minimum property requirements including HUD Code compliance, permanent foundation installation, classification as real property, and appropriate land ownership or long-term lease arrangements. These standards ensure veterans receive quality housing deserving of their military service sacrifice.
The home must be your primary residence rather than investment property or vacation home. This occupancy requirement aligns with VA’s mission supporting veterans’ homeownership goals rather than facilitating investment portfolios. Single-unit manufactured homes qualify most readily, though some multi-section configurations receive approval when meeting all program standards.
Calculate your potential VA loan payments using our specialized calculators. Review how other veterans successfully purchased manufactured homes in our VA loan case studies showing real-world application of these benefits.
Zero Down Payment Advantages
The VA loan’s zero down payment benefit creates extraordinary opportunities for veterans purchasing manufactured homes. Without requiring substantial savings for down payments, eligible borrowers can achieve homeownership sooner while preserving cash reserves for emergencies, home improvements, or other financial priorities.
This financing structure proves particularly valuable when purchasing manufactured homes in areas with affordable housing markets. The combination of zero down payment, no private mortgage insurance requirements, and competitive interest rates creates monthly payment obligations often substantially lower than rental costs for comparable housing.
Veterans purchasing manufactured homes through VA financing gain immediate homeownership equity as properties appreciate, building long-term wealth impossible through continued renting. The program recognizes manufactured housing as legitimate pathways to homeownership deserving full VA benefit support.
Funding fees apply to most VA loans, though these costs can be financed into loan amounts rather than requiring upfront cash payments. Disabled veterans may qualify for funding fee exemptions, further enhancing affordability. Use the VA calculator to model complete payment obligations including all applicable fees.
Land and Title Considerations
VA manufactured home loans require either land ownership or acceptable long-term leases supporting mortgage collateral protection. When purchasing homes in land-lease communities, lease terms must extend sufficiently beyond loan maturity dates, providing lenders assurance that land access remains secure throughout the financing period.
Homes must be titled as real property rather than personal property for VA mortgage financing. This title conversion process varies by state but generally requires permanent foundation installation, removal of transportation components, and proper recording of the property with local authorities as real estate rather than personal property.
Some states streamline title conversion processes while others impose more complex requirements. Understanding your state’s specific procedures helps you plan appropriately for title conversion costs and timeline requirements. Many manufactured home dealers and specialized contractors guide buyers through these processes when necessary.
If you’re purchasing land simultaneously with the manufactured home, VA financing can sometimes bundle both acquisitions into single mortgages. This approach simplifies financing while ensuring proper title establishment from the beginning. Your lender can advise whether combined land-and-home financing makes sense for your situation.
USDA Rural Housing Loans: Zero Down in Eligible Areas
Geographic Eligibility Requirements
USDA loan programs support manufactured home purchases in designated rural and suburban areas meeting population density requirements. These geographic restrictions ensure program resources support rural housing development rather than subsidizing purchases in metropolitan areas served by conventional financing markets.
Many areas buyers might not consider “rural” actually qualify for USDA financing, including suburban communities surrounding mid-sized cities and small towns throughout the United States. USDA provides online mapping tools allowing prospective buyers to verify address eligibility before beginning home searches.
Manufactured homes represent ideal housing solutions in many USDA-eligible areas where new construction costs make traditional site-built homes financially challenging. The combination of zero down payment USDA financing with affordable manufactured housing creates homeownership opportunities for working families throughout rural America.
Geographic requirements change periodically as population patterns shift. Areas losing USDA eligibility typically grandfather existing loans while new purchases require alternative financing. Conversely, areas gaining eligibility open new opportunities for buyers previously unable to access zero down payment programs.
Use the USDA loan calculator to model payment scenarios in eligible areas. See how other families successfully used USDA financing for manufactured homes in our case studies demonstrating program application.
Income Limits and Property Standards
USDA manufactured home loans impose household income limits ensuring program resources support moderate-income families rather than high-earning households capable of conventional financing. Income limits vary by county based on median income data and household size, with higher limits in expensive housing markets.
These income calculations include all household members’ income, not just borrowers on the mortgage application. Understanding how USDA evaluates total household income helps you determine eligibility before investing significant time in the application process. Many families earning comfortable middle-class incomes still qualify, especially in higher-cost areas.
Property standards for manufactured homes parallel requirements under FHA and VA programs—permanent foundation installation, HUD Code compliance, real property title status, and appropriate land ownership arrangements. Homes must serve as primary residences rather than investment properties or vacation homes.
Property values cannot exceed area loan limits ensuring USDA resources support modest, appropriate housing rather than luxury properties. These limits, though varying by location, accommodate quality manufactured homes meeting family needs without excessive extravagance. Most modern manufactured homes easily fall within USDA value parameters.
Zero Down Payment Benefits
USDA’s zero down payment feature combined with no monthly mortgage insurance creates powerful affordability for rural manufactured home buyers. This benefit structure rivals VA programs while serving broader populations including non-veterans meeting income and location requirements.
The program charges upfront guarantee fees, typically financed into loan amounts rather than requiring cash payments at closing. This financing structure means eligible buyers can achieve homeownership with minimal closing costs, dramatically reducing barriers to homeownership for working families.
Monthly payment obligations under USDA financing often compare favorably to rental costs for similar housing, creating immediate financial benefits alongside long-term wealth building through homeownership. The combination of zero down payment and modest monthly obligations makes manufactured home ownership realistic for families previously unable to save for traditional down payments.
Calculate your potential payments using the USDA calculator, and explore refinancing options if you already own a manufactured home and want to improve your financing terms. The USDA cash-out refinance calculator shows how you might access equity while maintaining USDA’s favorable terms.
Conventional Mortgage Options for Manufactured Homes
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac Programs
Conventional financing through Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac secondary markets increasingly accommodates manufactured homes meeting strict property standards. These programs offer competitive rates and terms rivaling traditional site-built home financing when manufactured homes satisfy all qualification criteria.
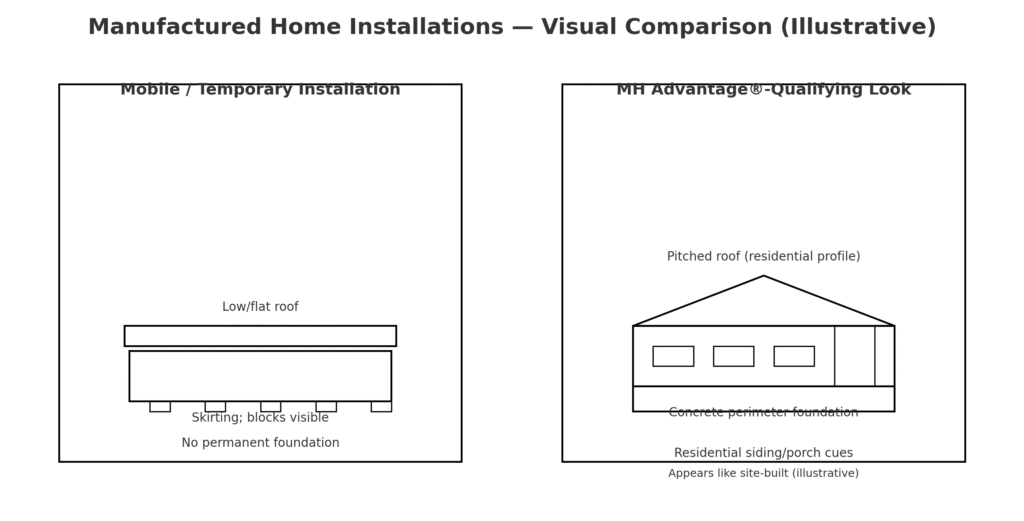
MH Advantage and similar programs recognize modern manufactured homes as quality construction deserving conventional mortgage support. These initiatives acknowledge improvements in manufactured housing construction standards, design aesthetics, and long-term value retention, opening doors to broader financing options beyond government-backed programs.
Manufactured homes financed through conventional mortgages must meet comprehensive standards including permanent foundation installation, minimum square footage requirements, design characteristics resembling site-built construction, HUD Code compliance, and real property title status. These requirements ensure homes meet secondary market investors’ quality and value standards.
Properties cannot be located in land-lease communities for conventional financing—borrowers must own the land beneath manufactured homes. This requirement reflects secondary market concerns about collateral protection and property value preservation when land ownership separates from home ownership.
Use the conventional loan calculator to model payment scenarios and compare with government-backed alternatives. Review our conventional loan case studies to see how other borrowers successfully navigated this financing path.
Down Payment and PMI Requirements
Conventional manufactured home loans typically require larger down payments than government-backed alternatives, often starting around the same minimums as traditional conventional mortgages but sometimes requiring slightly more based on property characteristics and lender overlays.
Private mortgage insurance applies when down payments fall below conventional thresholds, adding to monthly payment obligations but enabling homeownership with smaller initial cash investments. PMI costs eventually cancel once equity reaches appropriate levels through principal paydown and appreciation, unlike government-backed programs with permanent or upfront insurance costs.
Credit score requirements for conventional financing generally exceed government program minimums, reflecting secondary market investor standards for loan quality and default risk management. Strong credit profiles access the most favorable terms while moderate credit may face higher rates or larger down payment requirements.
Debt-to-income ratios follow conventional guidelines but may face tighter restrictions for manufactured homes compared to site-built properties. Lenders evaluate your complete financial picture ensuring comfortable payment management alongside existing obligations. Conservative borrowing within comfortable ratios supports long-term homeownership success.
MH Advantage Program Benefits
The MH Advantage program represents Fannie Mae’s recognition that modern manufactured homes deserve conventional mortgage treatment when meeting specific construction and aesthetic standards. This program specifically targets newer manufactured homes incorporating design features making them virtually indistinguishable from site-built construction.
Qualifying homes must include features like pitched roofing similar to traditional homes, residential-style siding materials, minimum square footage requirements, attached garages or carports when applicable, and overall curb appeal matching surrounding site-built neighborhoods. These standards ensure homes maintain values supporting long-term mortgage investments.
MH Advantage offers down payment flexibility sometimes lower than traditional manufactured home conventional financing, acknowledging that qualifying properties represent lower risk investments for secondary market investors. This recognition of quality construction translates to better terms for borrowers purchasing modern, well-designed manufactured homes.
Properties must be permanently installed on owned land with proper foundation systems and real property titles. The combination of quality construction, permanent installation, and land ownership creates mortgage collateral closely approximating traditional real estate, justifying favorable conventional financing terms.
Manufactured Homes in Land-Lease Communities
Community-Specific Financing Challenges
Manufactured homes in land-lease communities face unique financing challenges since borrowers own homes but lease land underneath. This ownership separation creates complications for mortgage lenders requiring real property collateral securing loans against both structures and underlying land.
Many traditional mortgage programs, particularly conventional financing, prohibit lending on land-lease properties due to concerns about lease term expiration, potential rent increases affecting affordability, and complications with foreclosure procedures if land access terminates. These restrictions limit financing options for many manufactured home buyers.
However, some FHA and VA programs do accommodate land-lease situations when leases meet specific requirements including sufficient term lengths extending well beyond mortgage maturity dates. These programs recognize that stable, well-managed manufactured home communities provide quality housing options deserving financing support.
Chattel loans represent another financing path for land-lease properties, treating manufactured homes as personal property rather than real estate. While terms and rates typically prove less favorable than real property mortgages, chattel financing makes homeownership accessible when traditional mortgages aren’t available.
Lease Requirements for Mortgage Approval
When pursuing mortgage financing for manufactured homes in land-lease communities, lease terms must satisfy lender requirements protecting mortgage investments. Leases must extend substantially beyond mortgage terms—often requiring lease durations of thirty to fifty years or more ensuring property access throughout the entire financing period.
Lease agreements must include specific provisions protecting lenders’ interests if borrowers default on mortgages. These provisions typically grant lenders rights to assume leases, continue payments, and maintain property access during foreclosure proceedings. Without such protections, lenders cannot offer traditional mortgage financing.
Community owners must agree to notify lenders of any lease defaults or termination notices, providing opportunities for lenders to cure defaults and protect their collateral investments. This communication requirement ensures lenders can intervene preventing property loss through lease terminations.
Lease payment amounts and escalation clauses receive scrutiny during underwriting processes. Lenders evaluate whether lease payments combined with mortgage payments create sustainable housing costs within affordable debt-to-income ratios. Excessive or rapidly escalating lease payments may prevent mortgage approval even when homes otherwise qualify.
Community Reputation and Stability
Lenders evaluate manufactured home community reputation, management quality, and financial stability when considering mortgage applications. Well-maintained communities with professional management and stable ownership access financing more readily than communities with maintenance issues, management turnover, or uncertain futures.
Community amenities, upkeep standards, and resident demographics factor into lender decisions. Communities with higher owner-occupancy rates rather than heavy renter concentrations typically receive more favorable lending consideration, as owner-occupancy correlates with property value stability.
Some manufactured home communities maintain preferred lender relationships or approved lender lists where financing occurs more smoothly due to established working relationships and familiarity with community lease terms. Purchasing in such communities can streamline financing processes compared to communities where lenders have limited experience.
If you’re considering manufactured homes in land-lease communities, research community reputation and discuss financing options early in your home search. Understanding which lenders work comfortably with specific communities helps you identify viable financing paths before investing significant time in property selection.
Chattel Loans: Personal Property Financing
When Chattel Loans Make Sense
Chattel loans finance manufactured homes as personal property rather than real estate, similar to auto loans or RV financing. This financing structure accommodates situations where permanent foundation installation isn’t feasible, land ownership is separate from home ownership, or buyers prefer maintaining mobility options for relocating homes in the future.
Chattel loans avoid complex title conversion requirements and permanent foundation costs, creating simpler transaction processes in some circumstances. For buyers in land-lease communities unable to access traditional mortgages, chattel financing provides the only realistic path to homeownership rather than continued renting.
However, chattel loans typically carry higher interest rates than real property mortgages, reflecting greater risk for lenders and lack of land collateral securing loans. Terms generally run shorter than traditional mortgages, often capping at fifteen to twenty years rather than thirty-year periods standard with real property financing.
Down payment requirements for chattel loans often exceed traditional mortgage minimums, sometimes requiring substantial equity investments limiting affordability for first-time buyers. These requirements reflect lenders’ recognition that personal property collateral provides less security than real estate backed by land ownership.
Chattel Loan Terms and Rates
Interest rates on chattel loans typically run several percentage points higher than comparable conventional mortgages or government-backed programs, substantially increasing total borrowing costs over loan terms. This rate differential reflects the personal property nature of collateral and historical loss rates on manufactured home chattel lending.
Loan terms rarely extend beyond twenty years and frequently cap at fifteen years or less, creating higher monthly payments compared to thirty-year real property mortgages on similar loan amounts. These shorter terms, combined with higher rates, can strain affordability despite potentially lower home purchase prices.
Some chattel lenders impose prepayment penalties discouraging early loan payoff, though these provisions vary by lender and program. Borrowers planning to refinance into traditional mortgages after completing foundation installations and title conversions should carefully review prepayment penalty provisions before committing to chattel financing.
Credit requirements for chattel loans may prove more flexible than traditional mortgages in some cases, with specialized lenders serving borrowers unable to qualify for conventional or government-backed programs. This flexibility creates access to homeownership for buyers otherwise shut out of mortgage markets, though at considerably higher costs.
Converting Chattel Loans to Mortgages
Many borrowers initially finance manufactured homes through chattel loans while planning future conversions to traditional mortgages after completing permanent foundation installations and title conversions. This strategy provides immediate homeownership access while working toward better financing terms through subsequent refinancing.
The conversion process requires permanent foundation installation meeting HUD standards and lender requirements, title conversion from personal property to real property status, land purchase if not already owned, and qualification for traditional mortgage programs. Successfully completing these steps can dramatically reduce monthly payments and total borrowing costs.
Refinancing from chattel to mortgage status typically requires sufficient home equity supporting new mortgage loan-to-value requirements, adequate credit profiles qualifying for traditional programs, and income documentation meeting mortgage underwriting standards. Planning for these requirements helps ensure successful conversions when timing makes sense.
Some buyers use home equity products to finance foundation installations and title conversions once they’ve built equity through chattel loan paydown. This approach spreads conversion costs over time rather than requiring substantial upfront cash investments for improvements.
Refinancing Manufactured Homes: Improving Your Terms
Rate-and-Term Refinancing Opportunities
Manufactured homeowners with existing mortgages or chattel loans can pursue refinancing when market conditions or improved personal finances create opportunities for better terms. Rate-and-term refinancing replaces existing financing with new loans featuring lower interest rates, different term lengths, or both, potentially reducing monthly obligations or total interest costs.
Successful refinancing requires homes meeting current lending standards for permanent foundation installation, HUD Code compliance, real property title status, and adequate appraised values supporting new loan-to-value requirements. Homes initially financed through chattel loans may need foundation and title work before qualifying for traditional mortgage refinancing.
FHA refinancing programs, VA Interest Rate Reduction Refinance Loans, and conventional refinance options all accommodate manufactured homes meeting respective program standards. These programs provide pathways for improving financing terms when original purchase financing included less favorable rates or structures.
Use refinancing calculators for FHA, VA, and conventional programs to model potential payment savings and determine whether refinancing makes financial sense given closing costs and remaining loan terms.
Cash-Out Refinancing for Home Improvements
Cash-out refinancing allows manufactured homeowners to access equity built through appreciation and principal paydown, converting home equity into cash available for home improvements, debt consolidation, or other financial needs. This financing strategy proves particularly valuable when upgrading older manufactured homes or adding permanent improvements enhancing value and livability.
Lenders limit cash-out refinancing based on loan-to-value ratios and program guidelines, typically requiring substantial equity positions before approving equity access. VA cash-out programs and USDA cash-out options offer specific guidelines for eligible borrowers.
Cash-out refinancing can fund significant improvements like room additions, upgraded HVAC systems, energy efficiency enhancements, or aesthetic updates modernizing older manufactured homes. These improvements often increase property values, creating situations where equity extraction simultaneously improves homes while maintaining or even increasing equity positions through appreciation.
Alternative equity access through home equity lines of credit or home equity loans provides another strategy for accessing value without refinancing primary mortgages. Use the HELOC calculator or home equity loan calculator to explore these options.
Removing Mortgage Insurance Through Refinancing
Manufactured homeowners with FHA loans paying ongoing mortgage insurance premiums can potentially eliminate these costs through refinancing into conventional mortgages when equity positions and credit profiles support conventional qualification. This strategy saves thousands in insurance premiums over remaining loan terms.
The timing requires adequate equity through appreciation and principal paydown, credit scores meeting conventional standards, and home conditions satisfying conventional property requirements. When these factors align, refinancing from FHA to conventional programs eliminates mortgage insurance obligations while potentially securing better interest rates.
VA borrowers already benefit from no monthly mortgage insurance requirements, though they paid upfront funding fees. Refinancing VA loans through streamlined VA programs or conventional alternatives might make sense when substantial rate reductions justify transaction costs.
Calculate potential savings using payment comparison tools to determine whether refinancing for insurance removal makes financial sense. Consider how long you plan to remain in the home, as refinancing costs require sufficient time to recover through monthly savings before justifying transactions.
Foundation Requirements and Permanent Installation
HUD Permanent Foundation Guide
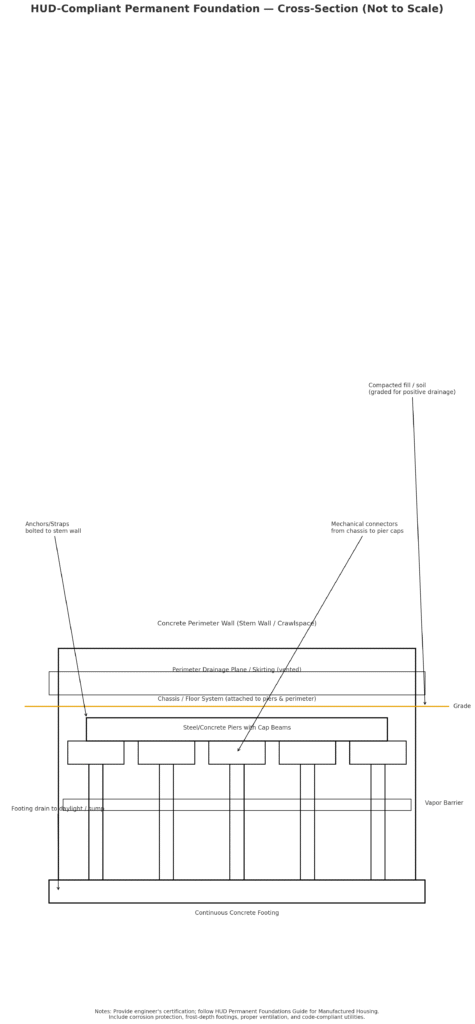
The HUD Permanent Foundations Guide for Manufactured Housing establishes comprehensive standards ensuring manufactured homes receive foundation systems providing stability, durability, and protection comparable to site-built construction. These standards create nationwide consistency in permanent foundation requirements supporting mortgage lending across state lines.
Permanent foundations must support the entire home structure distributing loads to underlying soil or rock, resist frost heave and settling in all climate conditions, provide adequate ventilation preventing moisture accumulation and structural damage, ensure proper drainage directing water away from foundation systems, and accommodate utility connections including plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems.
Foundation designs vary based on soil conditions, climate factors, local building codes, and specific home configurations. Common acceptable systems include poured concrete perimeter walls with concrete floor systems, concrete slab-on-grade foundations meeting thickness and reinforcement requirements, reinforced masonry foundations with proper footings and support systems, and engineered pier-and-beam systems with permanent connections.
Professional engineering certifications typically accompany permanent foundation installations, documenting designs meet HUD standards and local building code requirements. These certifications become crucial documents during mortgage applications, providing lenders assurance that foundations adequately support long-term property values justifying mortgage investments.
Installation and Certification Process
Permanent foundation installation requires licensed contractors familiar with manufactured home foundation requirements and local building codes. The process begins with proper site preparation including excavation, drainage installation, and soil compaction ensuring stable bases for foundation systems.
Foundation construction follows engineering specifications with regular inspections ensuring compliance with design requirements and building codes. Upon completion, jurisdictions typically require final inspections by local building officials verifying proper installation before issuing certificates of occupancy or foundation certifications.
Engineering certifications document that completed foundations meet HUD Permanent Foundations Guide specifications and adequately support manufactured homes throughout their useful lives. These certifications require professional engineer review of foundation designs, construction processes, and final installations confirming compliance with all applicable standards.
Installation costs vary significantly based on foundation types, site conditions, local labor markets, and home sizes. Budgeting for permanent foundation expenses requires local contractor estimates specific to your property and chosen foundation system. Some renovation loan programs can bundle foundation costs with home purchases when properties require foundation work.
Transportation Equipment Removal
Permanent foundation installation requires removing transportation components including wheels, axles, towing hitches, and other equipment designed for home mobility. This removal symbolizes and legally establishes homes as permanently installed real property rather than personal property capable of relocation.
Transportation equipment removal occurs after homes arrive at permanent sites and before or during foundation installation processes. Licensed contractors typically handle removal, ensuring proper disconnection without damaging home structures or utility systems. Removed components may have salvage value or require proper disposal according to local regulations.
Some jurisdictions require documentation of transportation equipment removal as part of title conversion processes from personal to real property. Photographs, contractor certifications, or inspection reports may serve as evidence supporting real property designation and mortgage qualification.
The combination of permanent foundation installation and transportation equipment removal creates legal and practical permanence supporting real property status. Homes become real estate improvements attached to land rather than personal property capable of relocation, fundamentally changing their legal status and financing options.

Title Conversion: Personal Property to Real Estate
State-by-State Title Conversion Process
Title conversion processes transforming manufactured homes from personal property to real property vary significantly across states, with each jurisdiction maintaining unique requirements, procedures, and documentation standards. Understanding your state’s specific process proves essential for successfully completing conversions supporting traditional mortgage qualification.
Some states streamline conversions through simple administrative processes requiring basic documentation and modest fees. Other states impose complex requirements involving multiple agencies, extensive documentation, surveys, inspections, and substantial costs. Researching your state’s procedures early in the home buying or refinancing process prevents surprises and allows appropriate planning.
Common elements across most states include permanent foundation installation certifications, transportation equipment removal documentation, land ownership verification, survey or plot plans showing home placement, and application to appropriate state agencies handling title conversions. Processing times vary from weeks to months depending on jurisdiction efficiency and application completeness.
Title conversion typically involves surrendering existing personal property titles issued by state motor vehicle or manufactured housing departments and receiving new real property documentation recorded with county property records offices. This recording creates public records establishing homes as real estate improvements rather than personal property.
Documentation Requirements
Successful title conversion requires comprehensive documentation supporting permanent installation status and real property designation. Required documents typically include original personal property titles or certificates of origin, permanent foundation certifications from licensed engineers, contractor affidavits confirming transportation equipment removal, land deeds or ownership documentation, surveys or site plans showing home placement on owned land, and completed application forms from appropriate state agencies.
Some states require additional items like photographs documenting permanent installation, building inspection approvals, utility connection certifications, or affidavits from local officials confirming property addresses and tax assessments. Gathering complete documentation before beginning applications streamlines processes and prevents delays requiring supplemental submissions.
Professional assistance from title companies, real estate attorneys, or specialized manufactured housing consultants can navigate complex state requirements ensuring complete, accurate applications. These professionals understand state-specific procedures and maintain relationships with reviewing agencies facilitating smoother conversion processes.
Costs for title conversion vary widely depending on state requirements, professional assistance needs, and specific property circumstances. Budgeting for conversion expenses should include application fees, survey costs, professional service fees, and recording charges. Some refinancing programs can accommodate conversion costs within transaction structures.
Benefits of Real Property Status
Real property designation dramatically expands manufactured home financing options, opening access to traditional conventional mortgages, FHA programs, VA benefits, and USDA rural housing loans. These programs offer superior terms including lower interest rates, longer repayment periods, and smaller down payment requirements compared to chattel financing.
Real property status supports property value appreciation more effectively than personal property titles. Homes titled as real estate participate in normal real estate market appreciation cycles, building equity through market gains in addition to mortgage principal reduction. This appreciation creates wealth-building opportunities impossible with personal property depreciation patterns.
Tax benefits potentially improve with real property status, as real estate property taxes may allow for different deductions than personal property taxes in some jurisdictions. Additionally, mortgage interest deductibility follows standard real estate rules, potentially providing tax advantages compared to personal property loan interest treatment.
Future marketability improves dramatically when manufactured homes carry real property titles and permanent foundations. Buyers access broader financing options making properties easier to sell, while real property status eliminates stigmas sometimes associated with manufactured housing titled as personal property.
Qualifying Income and Credit for Manufactured Home Financing
Income Documentation Standards
Income verification for manufactured home financing follows similar standards to traditional mortgage qualification, with lenders evaluating employment stability, income sustainability, and debt-to-income ratios ensuring comfortable payment management. FHA, VA, USDA, and conventional programs each maintain specific documentation requirements.
W-2 employees typically provide recent pay stubs, W-2 forms, and employment verification confirming job stability and income consistency. Lenders verify employment directly with employers ensuring information accuracy and catching potential fraud before closing loans.
Self-employed borrowers face additional documentation requirements including business tax returns, profit-and-loss statements, and sometimes business bank statements demonstrating income stability and sustainability. Bank statement loan programs offer alternative documentation paths for self-employed manufactured home buyers when traditional tax return analysis proves challenging.
Retirement income, social security benefits, pension payments, and investment income all qualify for mortgage qualification when properly documented through official statements, tax returns, or award letters. Disability income and VA benefits also support qualification when borrowers demonstrate income stability and sufficiency covering proposed housing payments.
Credit Score Requirements
Credit score requirements for manufactured home financing vary by program, with FHA loans typically offering the most flexible credit standards, followed by VA programs, USDA loans, and conventional mortgages imposing stricter requirements. Understanding minimum credit scores helps you determine which programs realistically support your qualification.
Recent credit history matters more than past credit problems when demonstrating creditworthiness. Lenders evaluate payment patterns over recent years, looking for consistent on-time payments and responsible credit management. Significant past credit events like bankruptcies or foreclosures require specific waiting periods before regaining mortgage eligibility, with timeframes varying by program.
Credit report errors can wrongly damage credit scores and undermine qualification. Reviewing credit reports well before applying for manufactured home financing allows time to dispute errors, correct inaccuracies, and ensure reports accurately reflect your credit management. Credit repair may take months, making early preparation essential for smooth qualification.
Some lenders overlay additional credit requirements beyond program minimums, potentially requiring higher scores than technically necessary. Shopping multiple lenders helps identify those offering the most flexible credit evaluation within program guidelines, particularly important for borrowers with marginal credit profiles.
Debt-to-Income Ratio Considerations
Debt-to-income (DTI) ratios measure monthly debt obligations against gross monthly income, providing lenders insight into your capacity for managing proposed mortgage payments alongside existing financial commitments. Programs establish maximum DTI limits though some flexibility exists for strong compensating factors.
Front-end DTI ratios evaluate proposed housing payments including principal, interest, property taxes, insurance, and any homeowners association fees against gross monthly income. This ratio ensures housing costs remain proportionate to income levels supporting comfortable payment management without overextension.
Back-end DTI ratios incorporate all monthly debt obligations—housing payments plus auto loans, student loans, credit card minimum payments, and other installment debt—compared to gross income. This comprehensive ratio provides complete pictures of borrowers’ financial obligations relative to income capacity.
Programs vary in maximum allowable DTI ratios, with FHA and VA programs sometimes accommodating higher ratios than conventional financing. Strong compensating factors like substantial cash reserves, excellent credit, or significant down payments can sometimes justify higher DTI ratios when other qualification aspects prove strong.
How Stairway Mortgage Simplifies Manufactured Home Financing
Access to Specialized Manufactured Home Lenders
Stairway Mortgage maintains relationships with lenders specializing in manufactured home financing across FHA, VA, USDA, and conventional programs. Our network includes lenders with deep expertise navigating manufactured housing’s unique requirements, from permanent foundation certifications to title conversion processes.
Many traditional lenders avoid manufactured home financing due to complexity and specialized knowledge requirements. Our broker model connects you with lenders who actively want manufactured housing business and understand program nuances enabling smooth approval processes. This specialized access creates competitive advantages impossible when working with general-purpose lenders lacking manufactured housing expertise.
We guide you through property requirement evaluations before you commit to purchases, helping identify potential qualification obstacles early in your home search. This proactive approach prevents disappointing situations where you’ve invested time and emotion in properties ultimately unable to secure financing due to foundation, title, or location issues.
Our team understands state-specific title conversion requirements, permanent foundation standards, and program variations across manufactured home lending. We connect you with contractors, engineers, and title professionals when needed, coordinating complete solutions rather than leaving you to navigate complex processes independently.
Program Comparison and Optimization
With access to FHA, VA, USDA, and conventional manufactured home programs, we compare options identifying which programs offer optimal terms for your specific situation. Down payment requirements, interest rates, monthly payment obligations, and long-term costs vary significantly across programs.
We calculate total costs including interest, insurance, and fees across program alternatives, helping you understand complete financial pictures rather than focusing solely on monthly payments. This comprehensive analysis reveals which programs truly offer best value over time you plan owning the home.
Our calculators for FHA, VA, USDA, and conventional programs allow you to model scenarios before committing to specific paths. We walk through calculations together, ensuring you understand trade-offs between different down payment levels, term lengths, and program choices.
For properties in land-lease communities or requiring title conversions, we identify viable financing paths when traditional options aren’t available. Our experience with chattel financing and specialized programs ensures you access some form of financing even in challenging situations.
Streamlined Application and Approval
Our technology platform and experienced team streamline manufactured home loan applications, delivering pre-approvals within 24 hours when complete documentation supports rapid evaluation. Fast pre-approvals create competitive advantages when making offers in active manufactured housing markets where multiple buyers compete for quality properties.
We coordinate with appraisers familiar with manufactured housing valuation, engineers certifying permanent foundations, and title companies handling complex title conversions. This coordination prevents delays and confusion when multiple specialized professionals must contribute to successful loan closings.
Our team reviews properties for program eligibility before you submit offers, identifying potential obstacles that could prevent financing approval. This proactive approach prevents wasted time pursuing properties ultimately unable to qualify, focusing your home search on realistically financeable opportunities.
Post-approval, we manage transactions from application through closing, maintaining communication with all parties ensuring smooth processes and timely closings. Our experience with manufactured housing’s unique requirements prevents last-minute surprises that could delay closings or jeopardize purchases.
Ongoing Support for Refinancing and Equity Access
Our relationships with manufactured homeowners extend beyond initial purchases. When market conditions or your financial situation creates refinancing opportunities, we help you evaluate whether rate-and-term refinancing, cash-out programs, or equity access products make sense.
We monitor your original financing against current market rates, proactively reaching out when refinancing opportunities appear that could save you money. This ongoing attention ensures you continually optimize financing rather than remaining locked into dated terms while better options exist.
For manufactured homeowners initially financed through chattel loans, we guide conversion processes helping you transition to traditional mortgage financing when you’ve completed permanent foundation installations and title conversions. This guidance maximizes your long-term financial benefits from manufactured home ownership.
Our commitment to your long-term success means we view each client relationship as ongoing rather than transactional. We’re here to answer questions, provide guidance, and support your housing finance needs throughout your homeownership journey.
Ready to Achieve Manufactured Home Ownership?
Manufactured home financing has evolved into a comprehensive ecosystem offering legitimate pathways to affordable homeownership through government-backed programs, conventional mortgages, and specialized lending solutions. Understanding which programs fit your situation, navigating permanent foundation requirements, managing title conversions, and accessing specialized lenders create successful outcomes.
Whether you’re purchasing your first home, upgrading living situations, or refinancing existing manufactured housing, the right financing structure makes homeownership achievable and sustainable. Programs like FHA, VA, and USDA loans offer down payment assistance and flexible qualification supporting families otherwise unable to achieve homeownership goals.
Stairway Mortgage’s specialized expertise in manufactured home financing, extensive lender network, and commitment to your success create competitive advantages impossible when working with general-purpose lenders unfamiliar with manufactured housing’s unique requirements. We guide you through every step from property evaluation through closing and beyond.
Contact Stairway Mortgage today to explore your manufactured home financing options. We’ll evaluate your situation, compare programs across our extensive lender network, calculate scenarios using specialized calculators, and create customized solutions supporting your homeownership goals. Let us show you how manufactured housing creates pathways to affordable homeownership with quality construction and comprehensive financing support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get an FHA loan for a manufactured home in a land-lease community?
Yes, FHA loans can finance manufactured homes in land-lease communities when leases meet specific requirements. The lease must extend at least three years beyond your mortgage term, include provisions protecting lenders’ interests if you default, grant lenders rights to assume the lease during foreclosure, and require community owners to notify lenders of any lease defaults. Not all land-lease communities offer leases meeting FHA requirements, so verify lease terms before pursuing properties in specific communities.
Do manufactured homes on permanent foundations qualify for conventional mortgages?
Yes, manufactured homes with permanent foundations meeting HUD standards can qualify for conventional financing when homes satisfy additional requirements. The home must be titled as real property rather than personal property, sit on land you own rather than lease, meet minimum square footage requirements, incorporate design features resembling site-built homes, and comply with HUD Code construction standards. Programs like Fannie Mae’s MH Advantage specifically target modern manufactured homes with residential aesthetics.
What’s the difference between a manufactured home and a mobile home?
“Mobile home” refers to manufactured housing built before June 15, 1976, prior to HUD Code implementation. “Manufactured home” describes housing built after June 1976 meeting federal HUD Code standards regulating construction quality, safety, and energy efficiency. This distinction matters for financing because many lenders restrict financing to HUD Code-compliant manufactured homes built after 1976, viewing older mobile homes as higher risk. Modern manufactured homes bear little resemblance to older mobile homes in construction quality and design.
Can veterans use VA loans to buy manufactured homes?
Yes, VA loan benefits extend to manufactured homes when properties meet program requirements including HUD Code compliance, permanent foundation installation, real property title status, and land ownership or acceptable long-term leases. Veterans enjoy zero down payment benefits, no private mortgage insurance requirements, and competitive interest rates when purchasing qualifying manufactured homes. VA loans offer some of the most attractive manufactured home financing terms available. Use the VA calculator to explore payment scenarios.
How long does title conversion from personal property to real property take?
Title conversion timelines vary significantly by state, ranging from a few weeks in states with streamlined processes to several months in jurisdictions with complex requirements. Factors affecting timing include state agency processing speeds, documentation completeness when applying, permanent foundation certification availability, survey requirements, and local government inspection schedules. Starting title conversion processes early—ideally before or during home purchases rather than afterward—prevents financing delays. Some states allow simultaneous closing and title conversion while others require conversion completion before mortgage funding.
Need a Pre-Approval Letter—Fast?
Buying a home soon? Complete our short form and we’ll connect you with the best loan options for your target property and financial situation—fast.
- Only 2 minutes to complete
- Quick turnaround on pre-approval
- No credit score impact
Got a Few Questions First?
Let’s talk it through. Book a call and one of our friendly advisors will be in touch to guide you personally.
Not Sure About Your Next Step?
Skip the guesswork. Take our quick Discovery Quiz to uncover your top financial priorities, so we can guide you toward the wealth-building strategies that fit your life.
- Takes just 5 minutes
- Tailored results based on your answers
- No credit check required
Related Posts
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get program updates and rate insights in your inbox.